两数之和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ;i < nums.length; i++) { if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])){ return new int []{map.get(target - nums[i]), i}; } map.put(nums[i], i); } return null ; } }
二分查找法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static int binarySearch (int [] a, int target) { int i = 0 , j = a.length - 1 ; while (i <= j) { int m = (i + j) >> 1 ; if (target < a[m]) { j = m - 1 ; } else if (target > a[m]) { i = m + 1 ; } else { return m; } } return -1 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static int binarySearch (int [] a, int target) { int i = 0 , j = a.length; while (i < j) { int m = (i + j) >> 1 ; if (target < a[m]) { j = m; } else if (target > a[m]) { i = m + 1 ; } else { return m; } } return -1 ; }
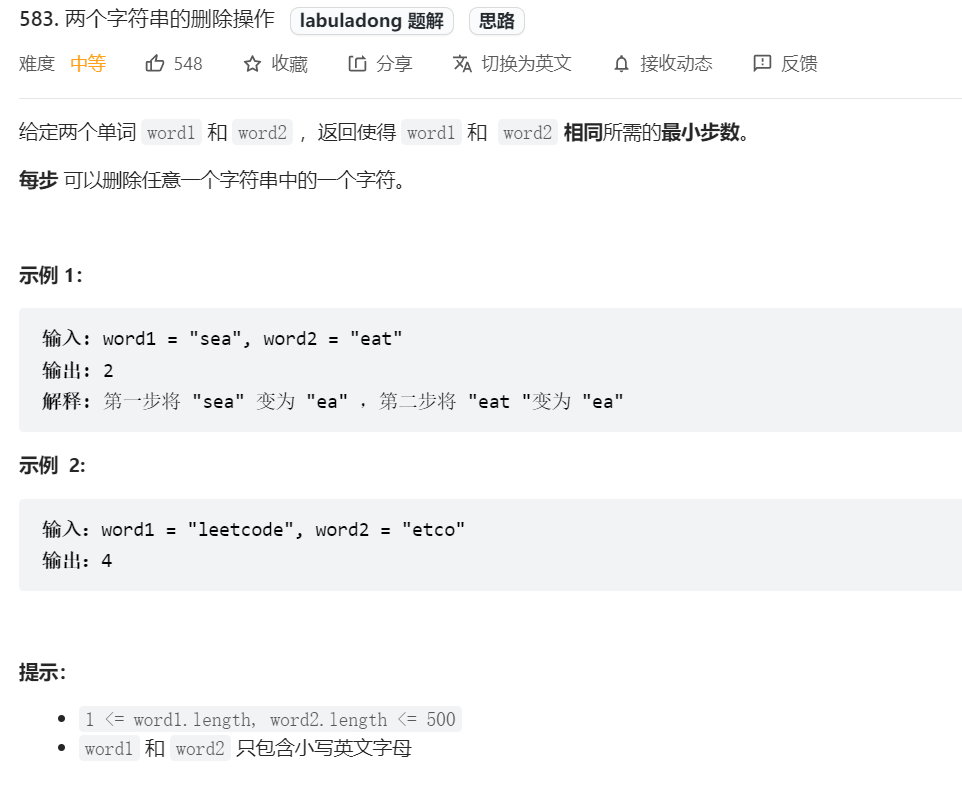
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int minDistance (String s1, String s2) { int m = s1.length(), n = s2.length(); int lcs = longestCommonSubsequence(s1, s2); return m - lcs + n - lcs; } int longestCommonSubsequence (String s1, String s2) { int m = s1.length(), n = s2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ;i <= m;i++){ for (int j = 1 ;j <= n;j++){ if (s1.charAt(i - 1 ) == s2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j-1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1 ], dp[i-1 ][j]); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
快速排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class QKSort { int n; public static void quick_sort (int q[], int l, int r) { if (l >= r) return ; int x = q[l], i = l - 1 , j = r + 1 ; while (i < j){ do i++;while (q[i] < x); do j--;while (q[j] > x); if (i < j) { int temp = q[i]; q[i] = q[j]; q[j] = temp; } } quick_sort(q, l, j); quick_sort(q, j + 1 , r); } public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); float v = (float ) (1e6 + 10 ); int q[] = new int [(int ) v]; int n = scanner.nextInt(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { q[i] = scanner.nextInt(); } quick_sort(q, 0 , n - 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { System.out.print(q[i] + " " ); } } }
归并排序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class MergeSort { static int v = 1000010 ; static int [] q = new int [v]; static int [] tmp = new int [v]; public static void merge_sort (int q[], int l, int r) { if (l >= r) return ; int mid = r + l >> 1 ; merge_sort(q, l, mid); merge_sort(q, mid + 1 , r); int k = 0 , i = l,j = mid + 1 ; while (i < mid && j <= r) if (q[i] <= q[j]) tmp[k++] = q[i++]; else tmp[k++] = q[j++]; while (i <= mid) tmp[k++] = q[i++]; while (j <= r) tmp[k++] = q[j++]; for (i = l,j = 0 ;i <= r;i++) q[i] = tmp[j]; } public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); Integer n = scanner.nextInt(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { scanner.nextInt(); } merge_sort(q, 0 , n - 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { System.out.print(q[i] + " " ); } } }
旋转数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 使用临时数组 public void rotate (int nums[], int k) { int length = nums.length; int temp[] = new int [length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { temp[i] = nums[i]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { nums[(i + k) % length] = temp[i]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 多次反转 public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { int length = nums.length; k %= length; reverse(nums, 0 , length - 1 ); reverse(nums, 0 , k - 1 ); reverse(nums, k, length - 1 ); } public void reverse (int [] nums, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { int temp = nums[start]; nums[start++] = nums[end]; nums[end--] = temp; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { int length = nums.length; k %= length; reverse(nums, 0 , length - k - 1 ); reverse(nums, length - k, length - 1 ); reverse(nums, 0 , length - 1 ); } public void reverse (int [] nums, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { int temp = nums[start]; nums[start++] = nums[end]; nums[end--] = temp; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 环形旋转 public static void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { int hold = nums[0 ]; int index = 0 ; int length = nums.length; boolean [] visited = new boolean [length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { index = (index + k) % length; if (visited[index]) { index = (index + 1 ) % length; hold = nums[index]; i--; } else { visited[index] = true ; int temp = nums[index]; nums[index] = hold; hold = temp; } } } 使用一个数组visited表示这个元素有没有被访问过,如果被访问过就从他的下一个开始,防止原地打转。
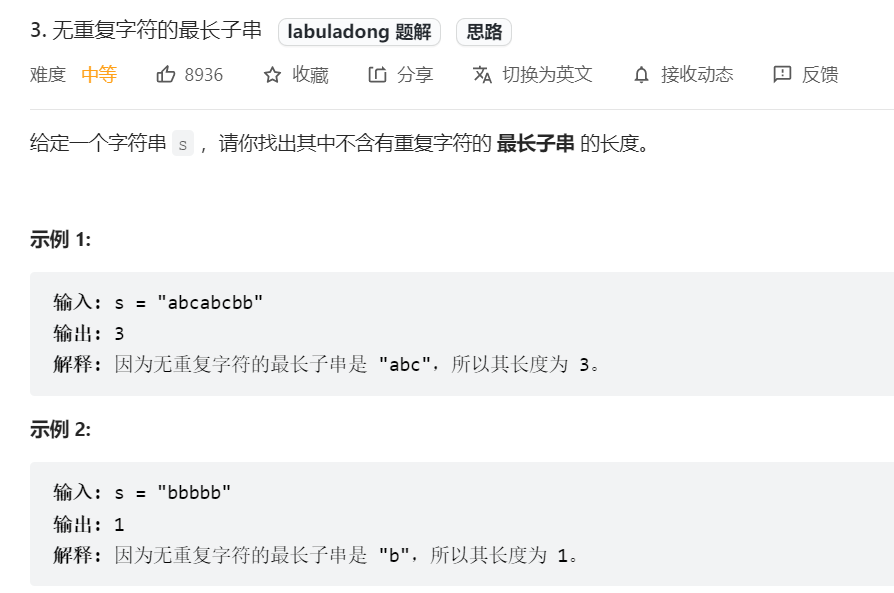
滑动窗口框架 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 void slidingWindow (string s, string t) { Map<Character,Integer> need = new HashMap <>(); Map<Character,Integer> window = new HashMap <>(); for (char c : t.toCharArray()) need.put(c, need.getOrDefault(c, 0 )+1 ); int left = 0 , right = 0 ; int count = 0 ; while (right < s.length()) { char c = s.charAt(right); right++; ... while (window needs shrink) { char d = s.charAt(left); left++; ... } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { Map<Character, Integer> window = new HashMap <>(); int left = 0 , right = 0 ; int res = 0 ; while (right < s.length()){ char c = s.charAt(right); right++; window.put(c, window.getOrDefault(c, 0 ) + 1 ); while (window.get(c) > 1 ){ char d = s.charAt(left); left++; window.put(d, window.get(d) - 1 ); } res = Math.max(res, right - left); } return res; } }
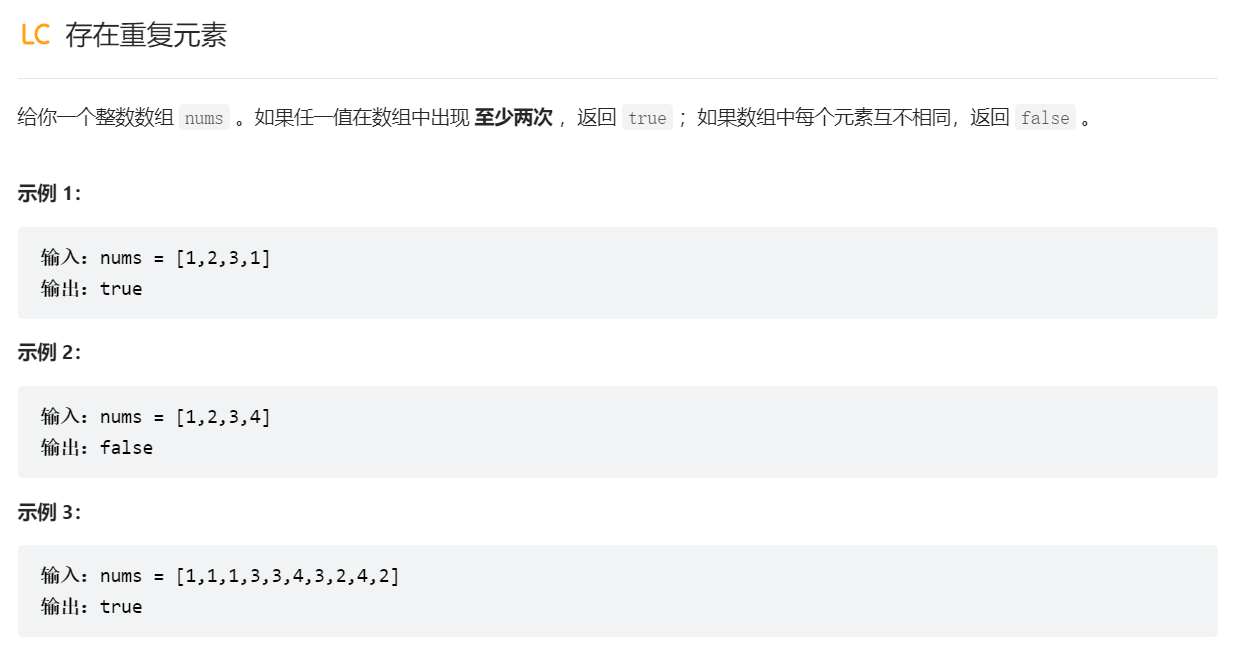
存在重复的元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public boolean containsDuplicate (int [] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int num : nums){ if (!set.add(num)) return true ; } return false ; } }
只出现一次的数字 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public int singleNumber (int [] nums) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ;i < nums.length;i++){ result ^= nums[i]; } return result; } }
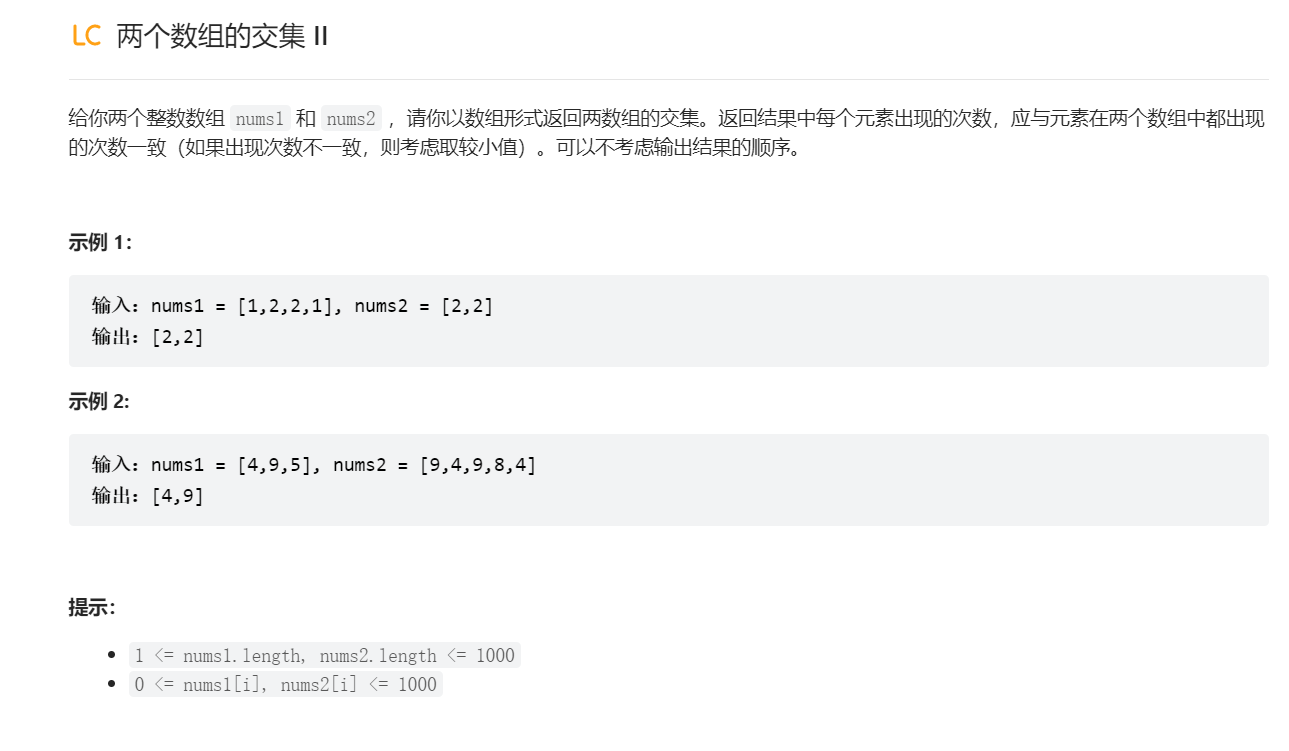
两个数组的交集
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public int [] intersect(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Arrays.sort(nums1); Arrays.sort(nums2); int i = 0 ; int j = 0 ; List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); while (i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length) { if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) { i++; } else if (nums1[i] > nums2[j]) { j++; } else { list.add(nums1[i]); i++; j++; } } int index = 0 ; int [] res = new int [list.size()]; for (int k = 0 ; k < list.size(); k++) { res[index++] = list.get(k); } return res; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public int [] intersect(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; i++) { map.put(nums1[i], map.getOrDefault(nums1[i], 0 ) + 1 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums2.length; i++) { if (map.getOrDefault(nums2[i], 0 ) > 0 ) { list.add(nums2[i]); map.put(nums2[i], map.get(nums2[i]) - 1 ); } } int [] res = new int [list.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { res[i] = list.get(i); } return res; }
加一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int [] plusOne(int [] digits) { int length = digits.length; for (int i = length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (digits[i] != 9 ) { digits[i]++; return digits; } else { digits[i] = 0 ; } } int temp[] = new int [length + 1 ]; temp[0 ] = 1 ; return temp; } }
移动零
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ) return ; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != 0 ) nums[index++] = nums[i]; } while (index < nums.length) { nums[index++] = 0 ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int i = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ;j < nums.length;j++){ if (nums[j] == 0 ) i++; else if (i != 0 ){ nums[j -i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = 0 ; } } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int i = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ;j < nums.length;j++){ if (nums[j] != 0 ){ int temp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[i]; nums[i] = temp; i++; } } } }
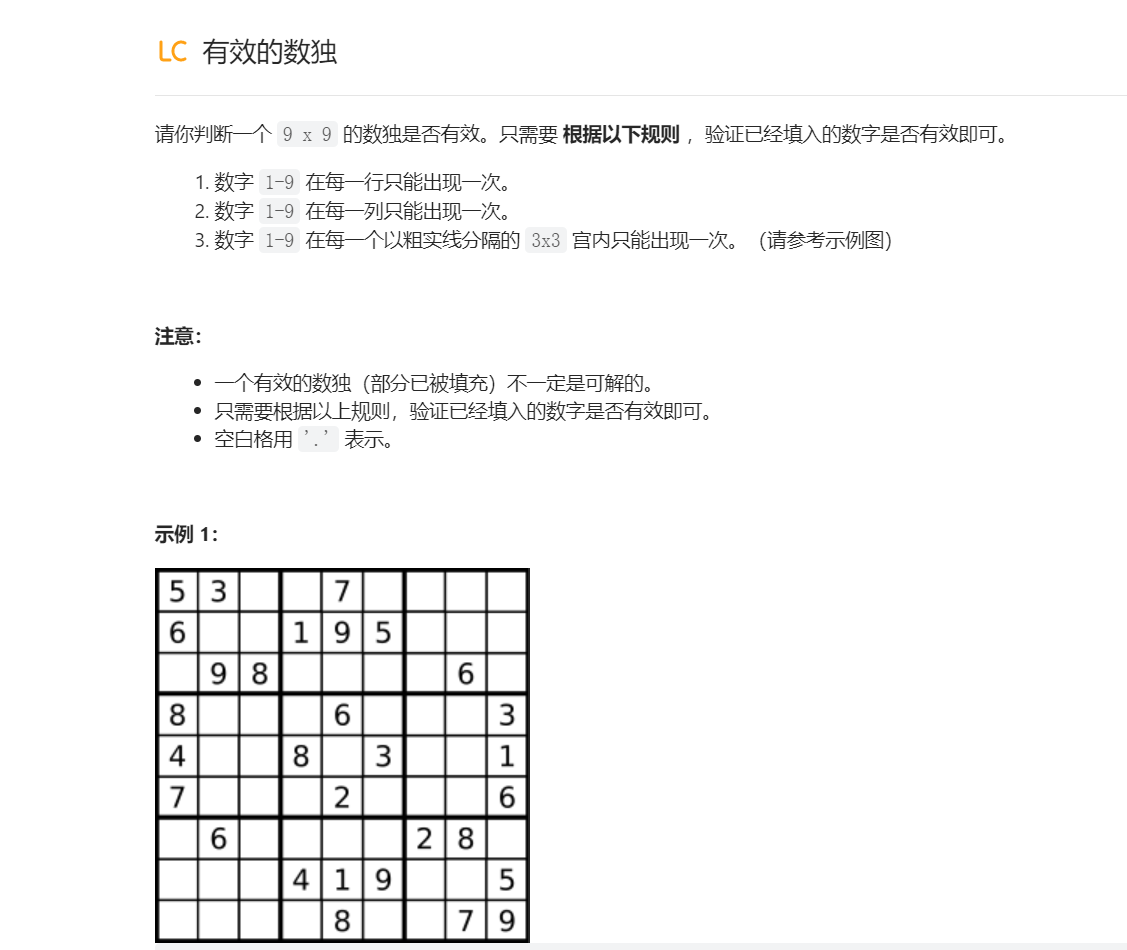
有效的数独
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution { public boolean isValidSudoku (char [][] board) { for (int i = 0 ;i < 9 ;i++){ boolean [] used = new boolean [10 ]; for (int j = 0 ;j < 9 ;j++){ if (board[i][j] == '.' ) { continue ; } int num = board[i][j] - '0' ; if (used[num]) { return false ; } used[num] = true ; } } for (int j = 0 ;j < 9 ;j++){ boolean [] used = new boolean [10 ]; for (int i = 0 ;i < 9 ;i++){ if (board[i][j] == '.' ) { continue ; } int num = board[i][j] - '0' ; if (used[num]) { return false ; } used[num] = true ; } } for (int i = 0 ;i < 3 ;i++){ for (int j = 0 ;j < 3 ;j++){ boolean [] used = new boolean [10 ]; for (int r = i*3 ;r < i * 3 + 3 ;r++){ for (int c = j * 3 ;c < j * 3 + 3 ;c ++){ if (board[r][c] == '.' ) { continue ; } int num = board[r][c] - '0' ; if (used[num]) { return false ; } used[num] = true ; } } } } return true ; } }
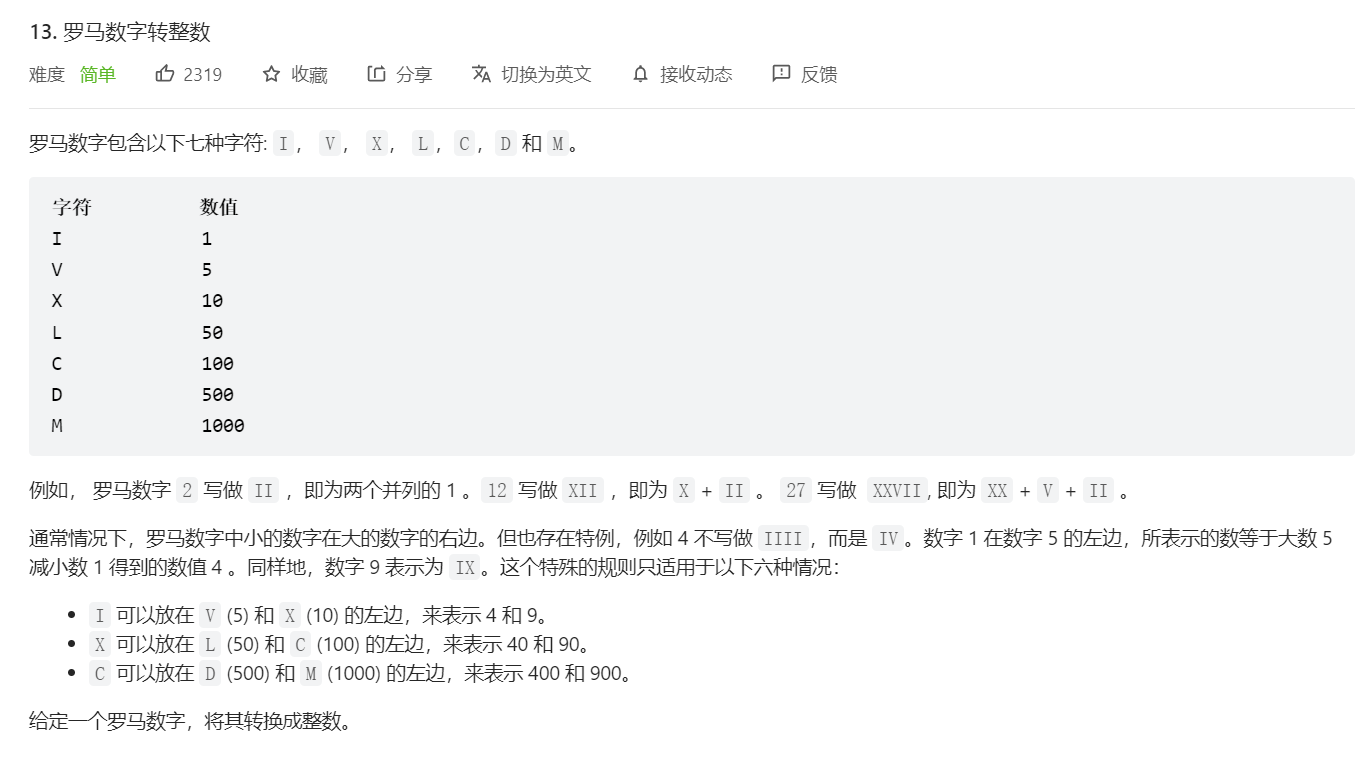
罗马数字转整数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int romanToInt (String s) { int num = 0 ; int perv = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i< s.length();i++){ int curr = 0 ; switch (s.charAt(i)){ case 'I' :curr = 1 ;break ; case 'V' :curr = 5 ;break ; case 'X' :curr = 10 ;break ; case 'L' :curr = 50 ;break ; case 'C' :curr = 100 ;break ; case 'D' :curr = 500 ;break ; case 'M' :curr = 1000 ;break ; } if (curr > perv){ num+=curr - perv * 2 ; }else { num += curr; } perv = curr; } return num; } }
有效的字母异位词
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { if (s.length() != t.length()) return false ; int [] letterCount = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) letterCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]++; for (int i = 0 ; i < t.length(); i++) letterCount[t.charAt(i) - 'a' ]--; for (int count : letterCount) if (count != 0 ) return false ; return true ; }
优化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { if (s.length() != t.length()) return false ; int [] letterCount = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) letterCount[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]++; for (int i = 0 ; i < t.length(); i++) { if (letterCount[t.charAt(i) - 'a' ] == 0 ) return false ; letterCount[t.charAt(i) - 'a' ]--; } return true ; }
先排序,在比较:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { char [] sChar = s.toCharArray(); char [] tChar = t.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(sChar); Arrays.sort(tChar); return Arrays.equals(sChar, tChar); }
一次遍历:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { if (s.length() != t.length()) return false ; char [] cs = s.toCharArray(); char [] ct = t.toCharArray(); int [] map = new int [26 ]; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < cs.length; i++) { if (++map[cs[i] - 'a' ] == 1 ) { count++; } if (--map[ct[i] - 'a' ] == 0 ) { count--; } } return count == 0 ; }
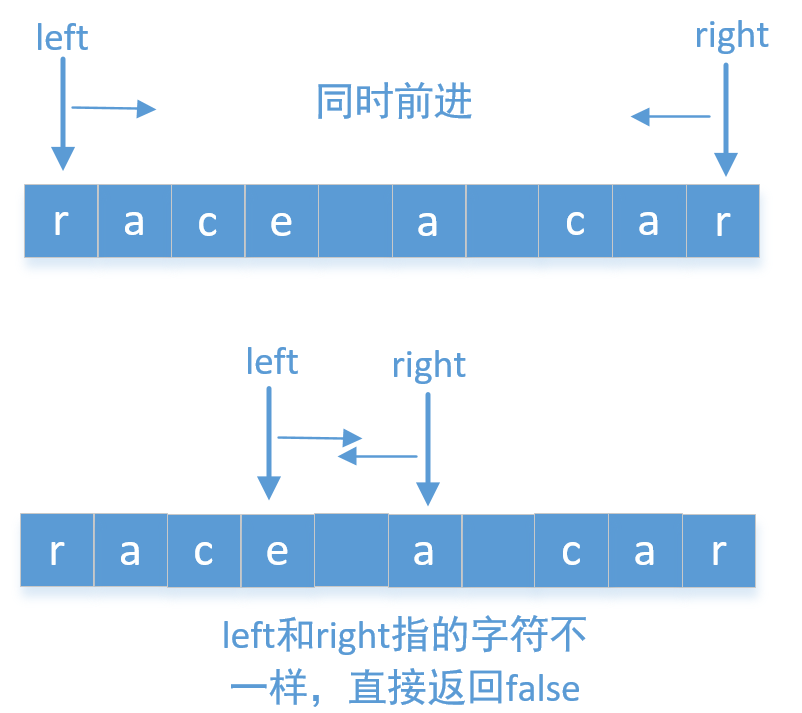
验证回文字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { if (s.length() == 0 ) return true ; int left = 0 , right = s.length() - 1 ; while (left < right) { while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(left))) left++; while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(right))) right--; if (Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(left)) != Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(right))) return false ; left++; right--; } return true ; } }
双指针的另一种写法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0 ) return true ; s = s.toLowerCase(); for (int i = 0 , j = s.length() - 1 ; i < j; i++, j--) { while (i < j && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(i))) i++; while (i < j && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(j))) j--; if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) return false ; } return true ; }
使用正则匹配:
1 2 3 4 5 public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { String actual = s.replaceAll("[^A-Za-z0-9]" , "" ).toLowerCase(); String rev = new StringBuffer (actual).reverse().toString(); return actual.equals(rev); }
递归方式实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { return isPalindromeHelper(s, 0 , s.length() - 1 ); } public boolean isPalindromeHelper (String s, int left, int right) { if (left >= right) return true ; while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(left))) left++; while (left < right && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(right))) right--; return Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(left)) == Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(right)) && isPalindromeHelper(s, ++left, --right); }
字符串转换整数 (atoi)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution { public int myAtoi (String s) { char [] chars = s.toCharArray(); int length = chars.length; int index = 0 ; while (index < length && chars[index] == ' ' ){ index++; } if (index >= length){ return 0 ; } int sign = 1 ; if (chars[index] == '-' || chars[index] == '+' ){ if (chars[index] == '-' ){ sign = -1 ; } index++; } int result = 0 ; int temp = 0 ; while (index < length){ int num = chars[index] - '0' ; if (num > 9 || num < 0 ){ break ; } temp = result; result = result * 10 + num; if (result/10 !=temp){ if (sign > 0 ){ return Integer.MAX_VALUE; }else { return Integer.MIN_VALUE; } } index++; } return result*sign; } }
实现 strStr() 暴力匹配:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int strStr (String haystack, String needle) { char [] hay = haystack.toCharArray(); char [] nee = needle.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i <= hay.length - nee.length; i++) { boolean found = true ; for (int j = 0 ; j < nee.length; j++) { if (hay[i+j] != nee[j]) { found = false ; break ; } } if (found) { return i; } } return -1 ; } }
一行代码搞定:
1 2 3 4 public int strStr (String haystack, String needle) { return haystack.indexOf(needle); } }
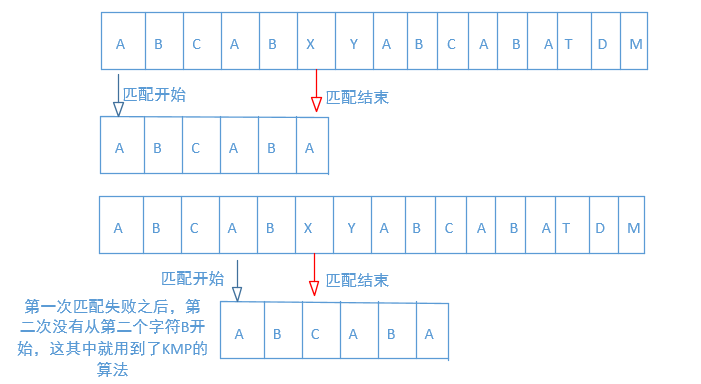
KMP算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 public int strStr (String haystack, String needle) { if (needle.length() == 0 ) return 0 ; int i = 0 ; int j = 0 ; int [] next = new int [needle.length()]; getNext(needle, next); while (i < haystack.length() && j < needle.length()) { if (j == -1 || haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; } else { j = next[j]; } if (j == needle.length()) return i - j; } return -1 ; } private void getNext (String p, int next[]) { int len = p.length(); int i = 0 ; int j = -1 ; next[0 ] = -1 ; while (i < len - 1 ) { if (j == -1 || p.charAt(i) == p.charAt(j)) { i++; j++; next[i] = j; } else j = next[j]; } }
x的n次幂
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution { public double myPow (double x, int n) { if (n == 0 ) { return 1 ; } long N = n; if (N < 0 ) { N = -N; x = 1 / x; } double ans = 1 ; while (N > 0 ) { if ((N & 1 ) == 1 ) { ans *= x; } x *= x; N >>= 1 ; } return ans; } }
每次循环中都会判断当前指数 N 是否为奇数,如果是奇数,则将结果乘上 x,否则只是将 x 自乘,然后将指数 N 右移一位。这样就可以通过不断将指数除以 2,来逐步计算 x 的指数幂,优化计算效率。
旋转数字 我们称一个数 X 为好数, 如果它的每位数字逐个地被旋转 180 度后,我们仍可以得到一个有效的,且和 X 不同的数。要求每位数字都要被旋转。
如果一个数的每位数字被旋转以后仍然还是一个数字, 则这个数是有效的。0, 1, 和 8 被旋转后仍然是它们自己;2 和 5 可以互相旋转成对方(在这种情况下,它们以不同的方向旋转,换句话说,2 和 5 互为镜像);6 和 9 同理,除了这些以外其他的数字旋转以后都不再是有效的数字。
现在我们有一个正整数 N, 计算从 1 到 N 中有多少个数 X 是好数?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int rotatedDigits (int n) { int count = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n;i++){ String s= String.valueOf(i); s = s.replaceAll("[+0, +1, +8]" , "" ); if (!"" .equals(s)){ s = s.replaceAll("[+2,+5,+6+,9]" ,"" ); if ("" .equals(s)){ count++; } } } return count; } }
找到所有好下标
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public List<Integer> goodIndices (int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); int count = 1 ; if (k == 1 ){ for (int i = 1 ;i < n - 1 ;i++){ res.add(i); } return res; } for (int i = 1 ;i < n - k - 1 ;i++){ if (nums[i] <= nums[i - 1 ] && nums[i + k + 1 ] >= nums[i + k]){ count++; if (count >= k) { res.add(i + 1 ); } }else { count = 1 ; } } return res; } }
最长公共前缀
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) { int m = strs.length; if (m == 0 ) return "" ; String ans = strs[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ;i < m;i++){ int j = 0 ; for (;j < ans.length() && j < strs[i].length();j++){ if (ans.charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j)){ break ; } } ans = ans.substring(0 , j); if (ans.equals("" )) return ans; } return ans; } }
将数组和减半的最少操作次数 给你一个正整数数组 nums 。每一次操作中,你可以从 nums 中选择 任意 一个数并将它减小到 恰好 一半。(注意,在后续操作中你可以对减半过的数继续执行操作)
请你返回将 nums 数组和 至少 减少一半的 最少 操作数。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 输入:nums = [5,19,8,1] 输出:3 解释:初始 nums 的和为 5 + 19 + 8 + 1 = 33 。 以下是将数组和减少至少一半的一种方法: 选择数字 19 并减小为 9.5 。 选择数字 9.5 并减小为 4.75 。 选择数字 8 并减小为 4 。 最终数组为 [5, 4.75, 4, 1] ,和为 5 + 4.75 + 4 + 1 = 14.75 。 nums 的和减小了 33 - 14.75 = 18.25 ,减小的部分超过了初始数组和的一半,18.25 >= 33/2 = 16.5 。 我们需要 3 个操作实现题目要求,所以返回 3 。 可以证明,无法通过少于 3 个操作使数组和减少至少一半。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution { public int halveArray (int [] nums) { PriorityQueue<Double> pq = new PriorityQueue <Double>((a, b) -> b.compareTo(a)); for (int num : nums){ pq.offer((double ) num); } int res = 0 ; double sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { sum += num; } double sum2 = 0.0 ; while (sum2 < sum / 2 ){ double x = pq.poll(); sum2 += x / 2 ; pq.offer(x / 2 ); res++; } return res; } }
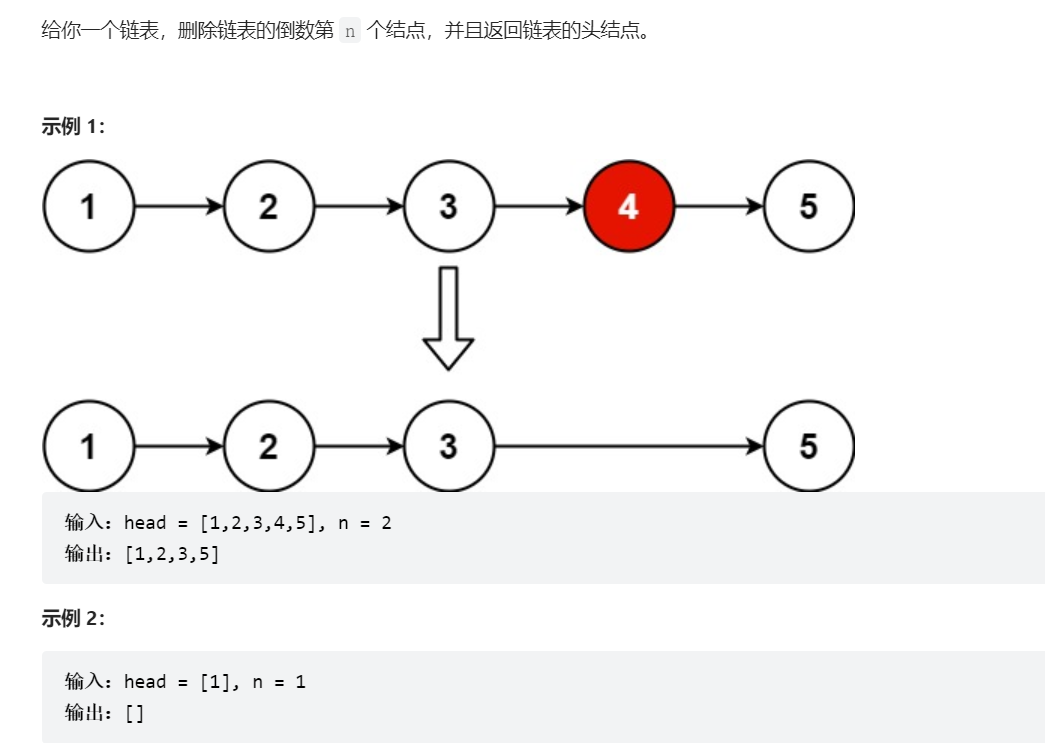
链表 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
提示:
链表中结点的数目为 sz
1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 ); dummy.next = head; ListNode fast = dummy; for (int i = 0 ;i < n;i++){ fast = fast.next; } ListNode slow = dummy; while (fast.next != null ){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } slow.next = slow.next.next; return dummy.next; } }
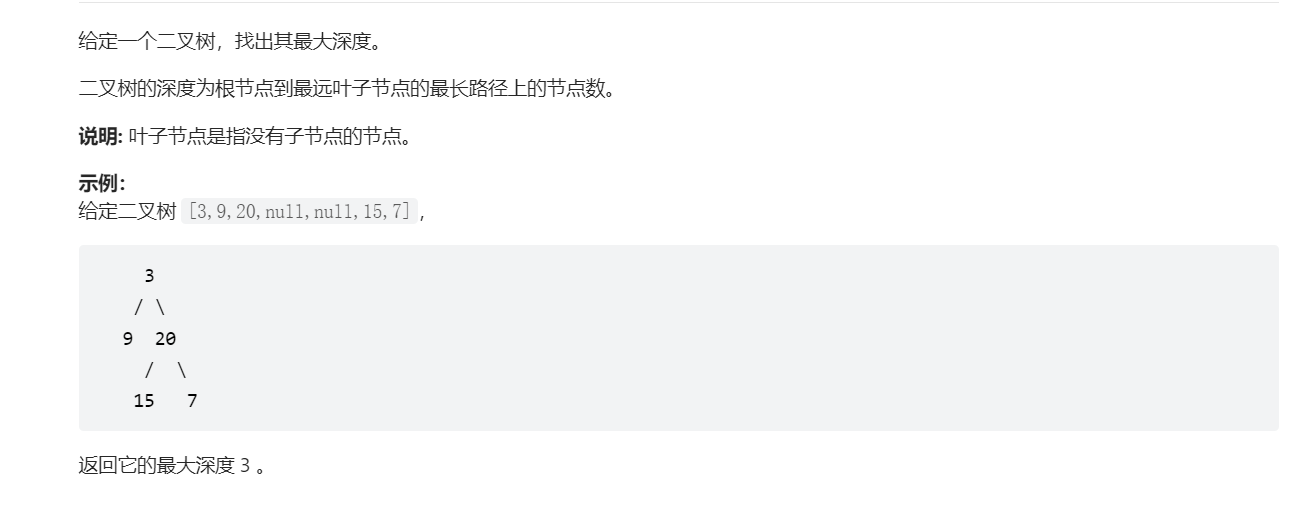
树 二叉树的最大深度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return 0 ; else { return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left)+1 , maxDepth(root.right)+1 ); } } }
验证二叉搜索树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { return isValidBST(root, null , null ); } public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root, Integer min, Integer max) { if (root == null ) return true ; if (min != null && root.val <= min) return false ; if (max != null && root.val >= max) return false ; return isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) && isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max); } }