软件结构发展史
单机时代-桌面应用
联机时代(Client-Server模式)
互联网时代(Browser-Server模式)
单机时代-桌面应用
桌面应用俗称单机应用,软件所有数据都保存在电脑本地硬盘中
优点:易于保存,结构简单
缺点:数据难以共享、安全性差、更新不及时

联机时代(Client-Server模式)
Client/Server结构(C/S结构)是指客户端和服务器结构
优点:数据方便共享,安全性高
缺点:必须安装客户端,升级与维护困难

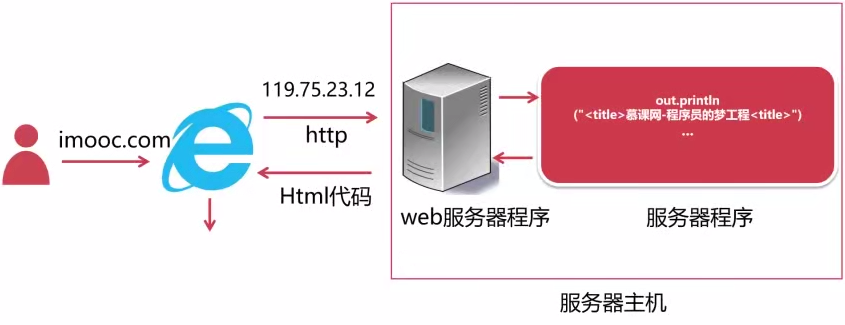
互联网时代(Browser-Server模式)
Broswer-Server(B/S)模式即浏览器和服务器模式
优点:开发简单,无需安装客户端,数据易于共享
缺点:相较于C/S模式,执行速度与用户体验相对较弱
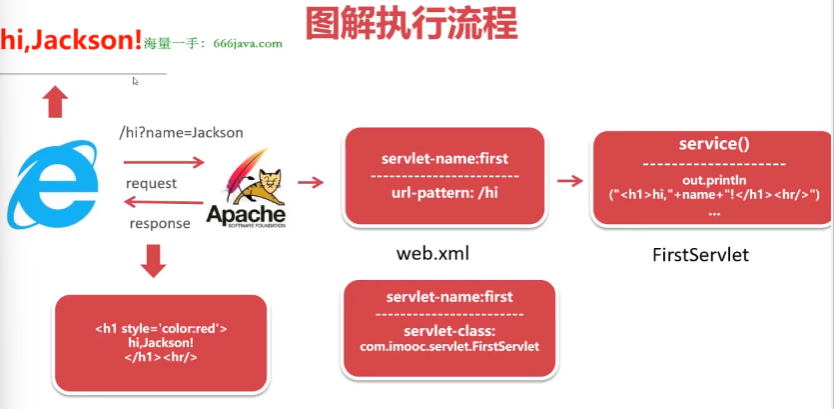
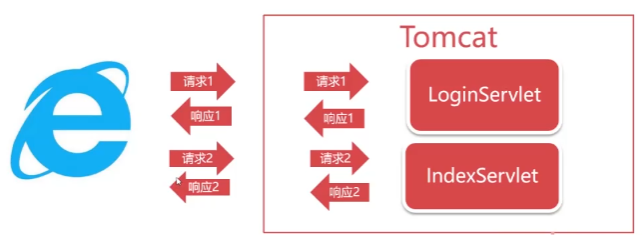
B/S模式执行流程


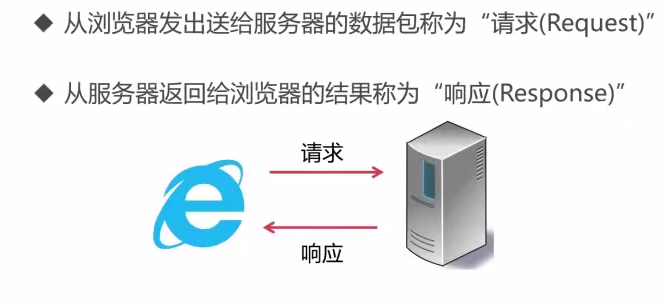
请求与响应

J2EE是什么
J2EE (Java 2 Platform Enterprise Edition) 是指”Java 2企业版”
B/S模式开发Web应用就是J2EE最核心的功能
J2EP由13个功能模块组成
J2EP中13个功能模块

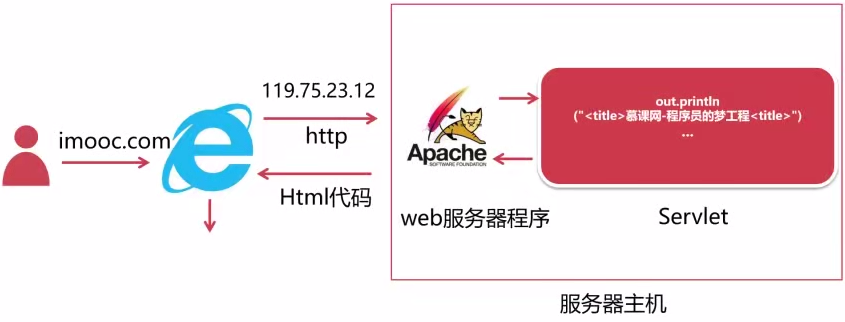
Servlet

Apache Tomcat

Tomcat与Servlet的关系


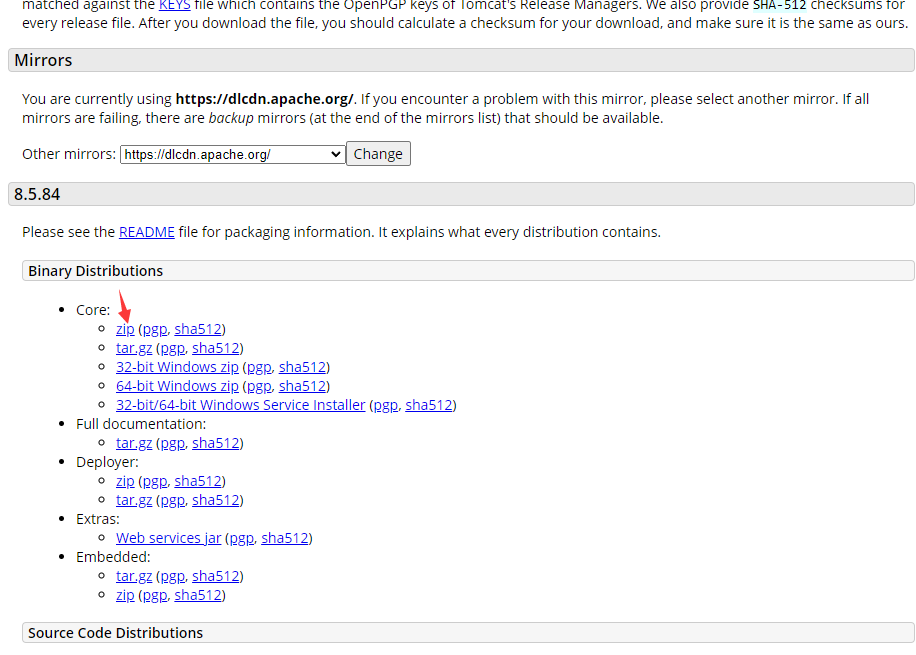
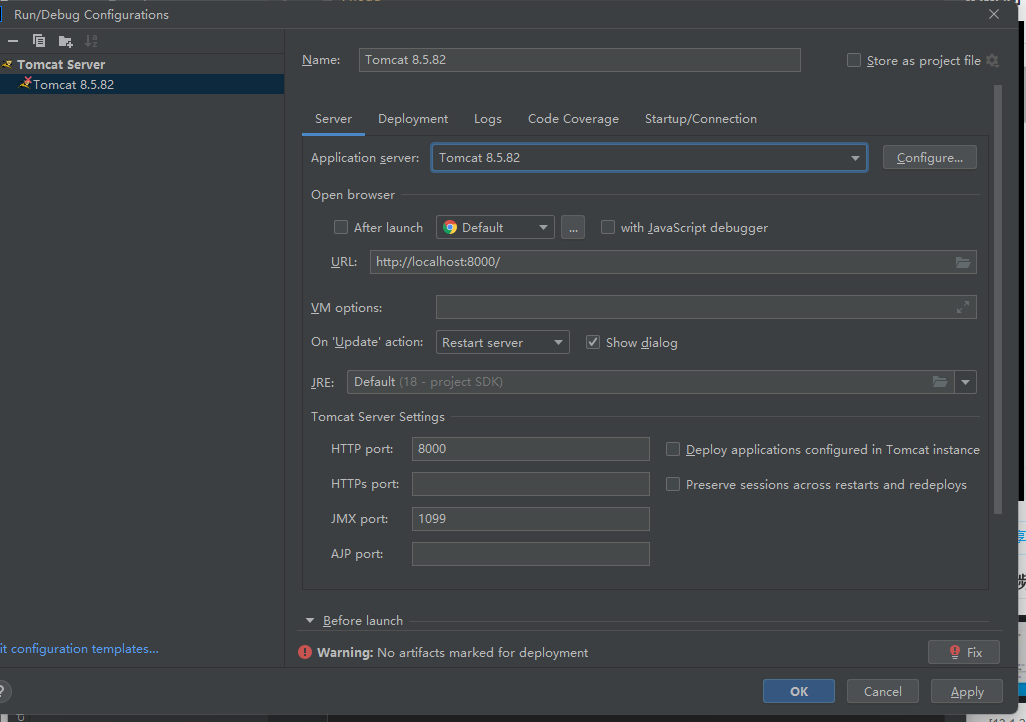
Tomcat安装与运行
官网:https://tomcat.apache.org/



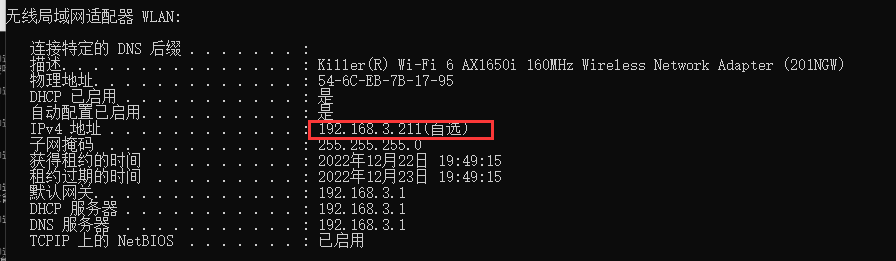
查询本机IP,在cmd中输入 ipconfig /all

浏览器上输入http://本机IP:8080/

或者直接输入 localhost:8080,就不用每次都去查IP。

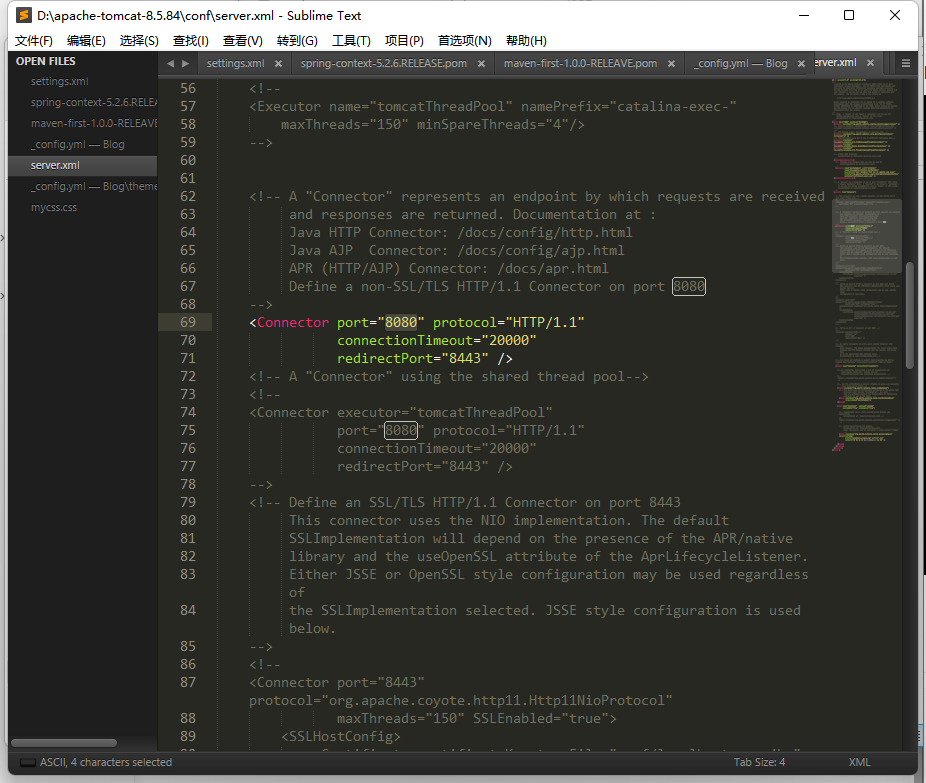
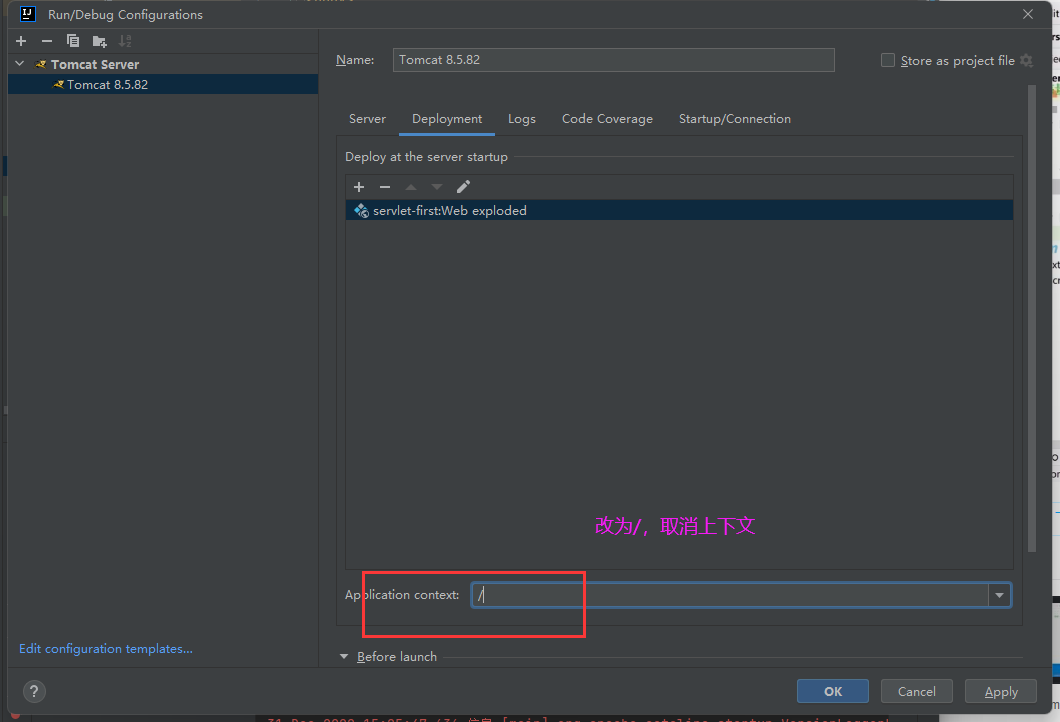
调整端口号,8080也可以改成8000,访问时也随之变化为localhost:8000
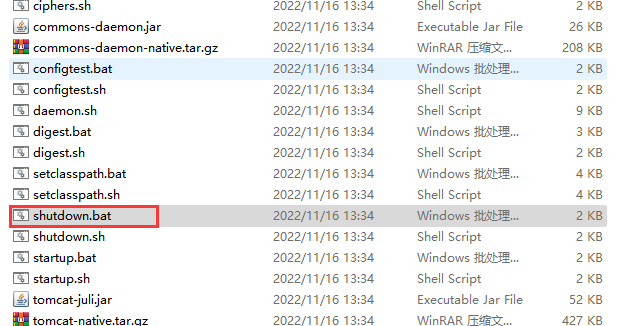
端口号被占用时,开启startup会发生闪退,错误发送到logs日志中。

点击shutdown关闭端口再启动就不会发生端口号占用情况。
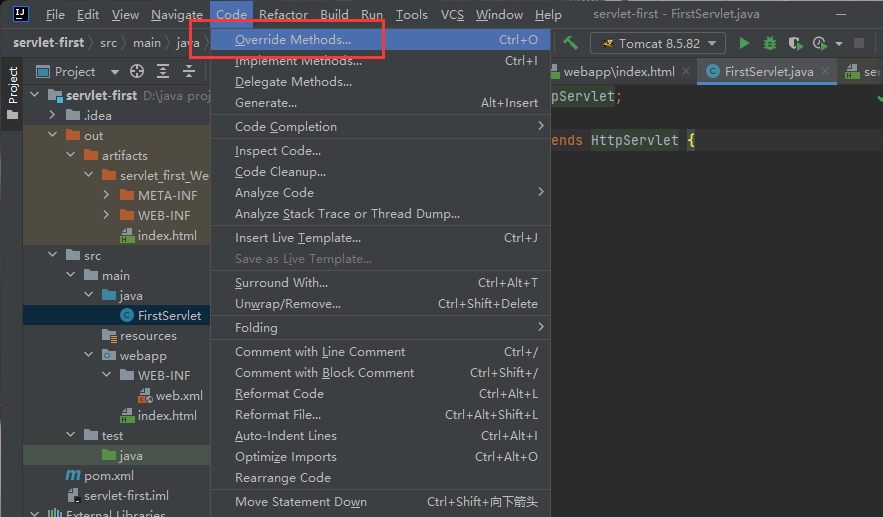
Servlet入门
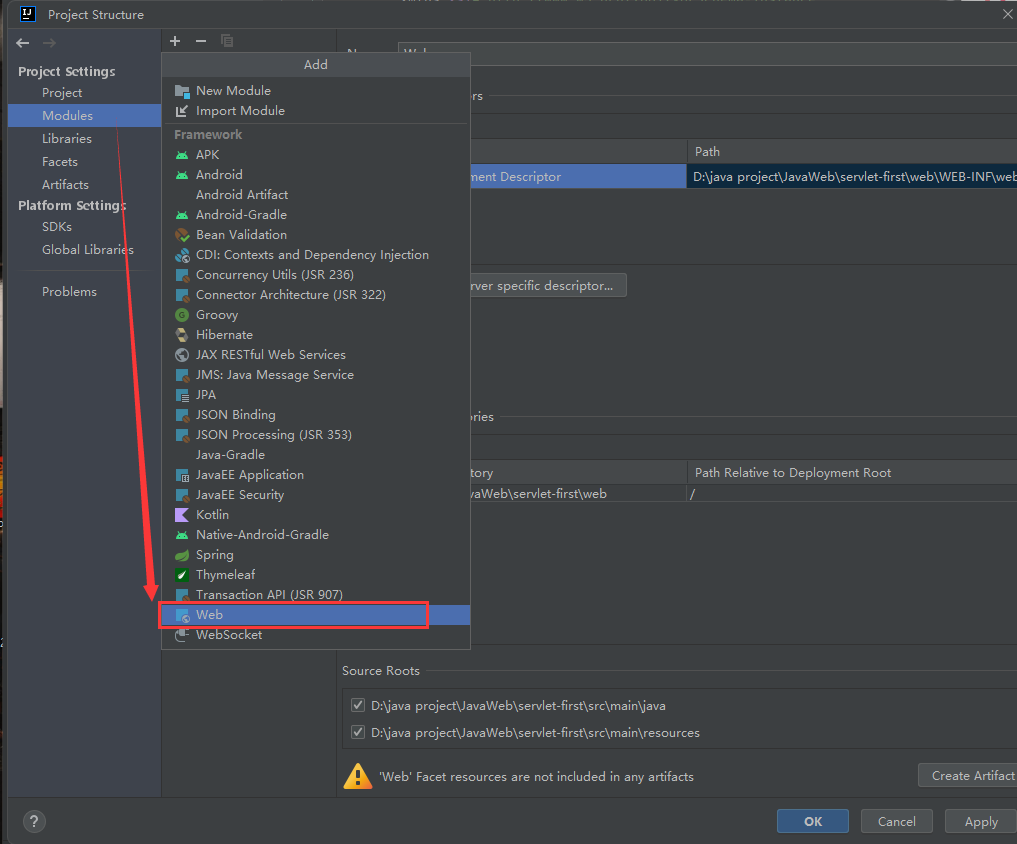
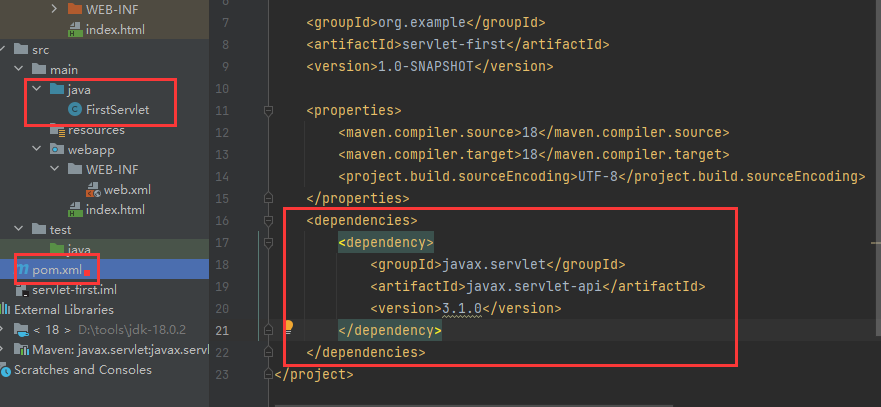
IDEA创建Java Web工程

https://tomcat.apache.org/whichversion.html

这里选3.1















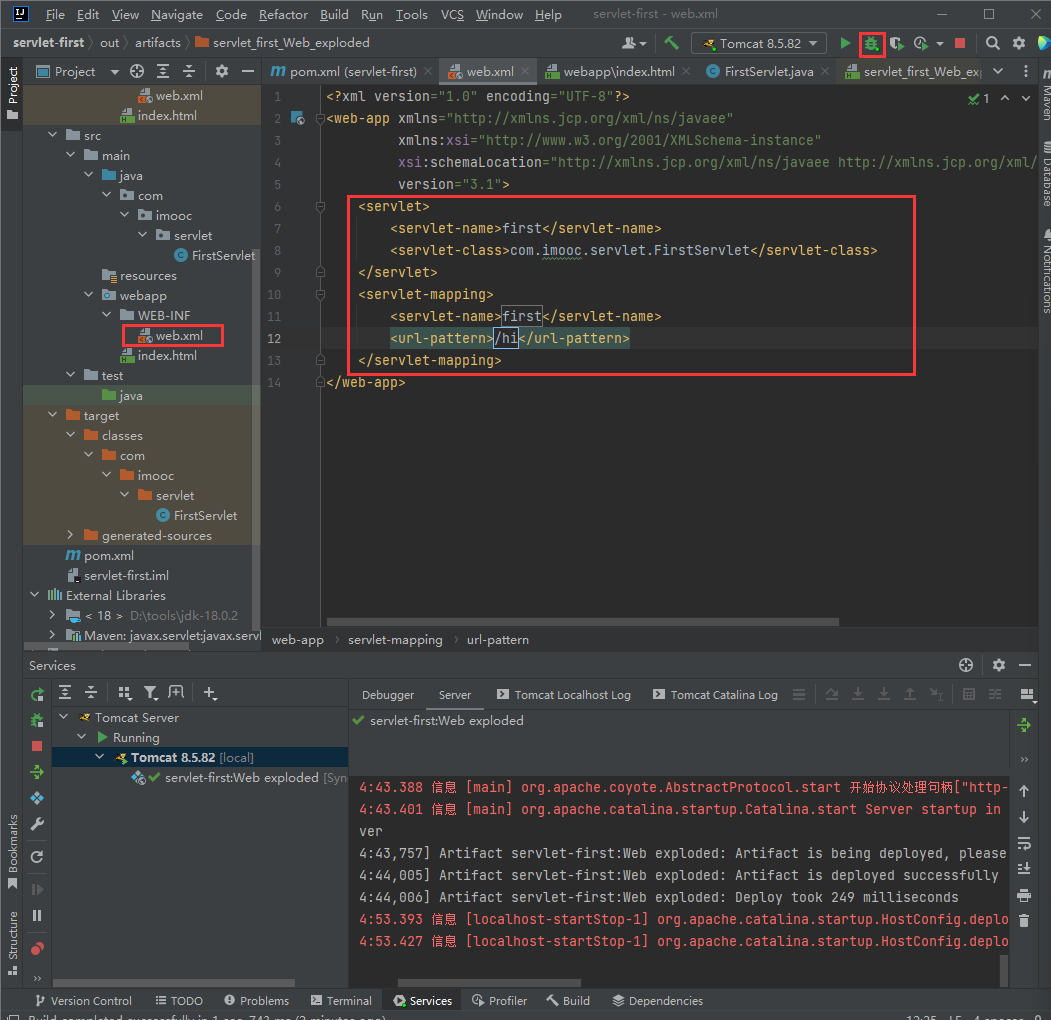
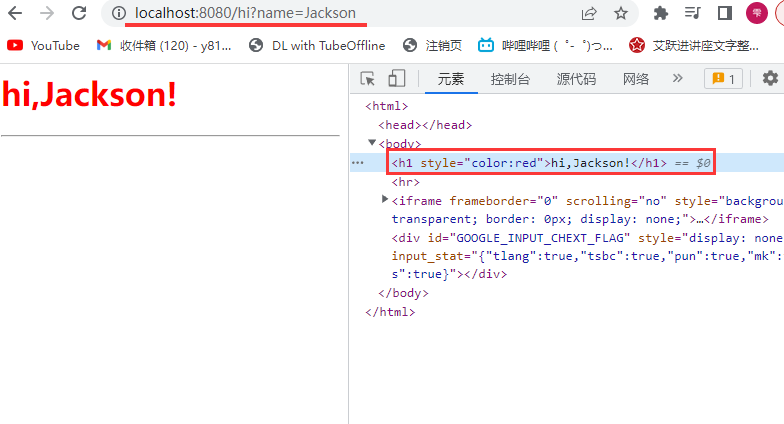
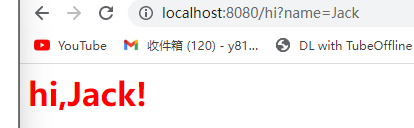
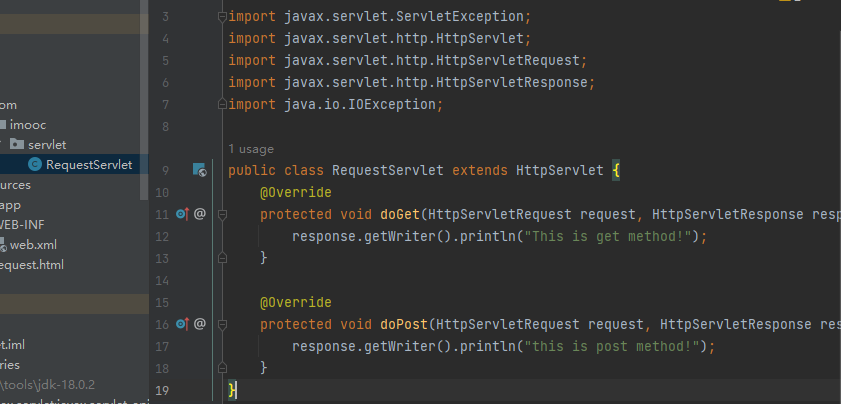
第一个Servlet







图解执行流程

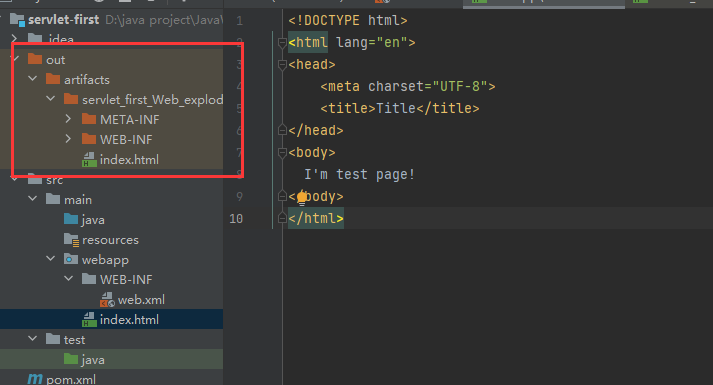
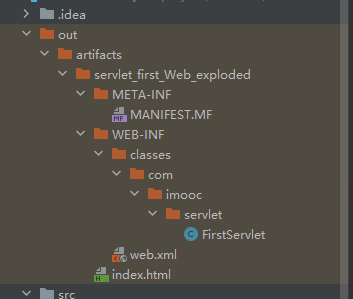
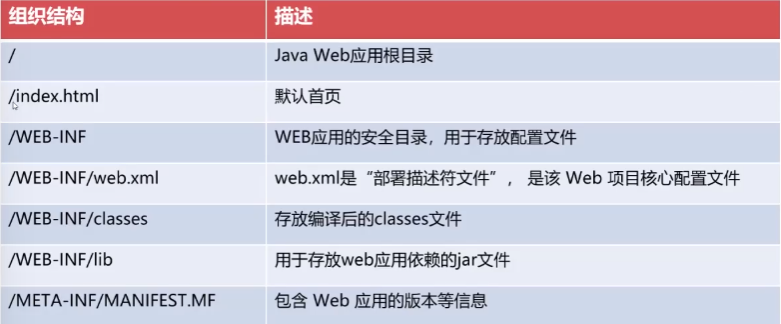
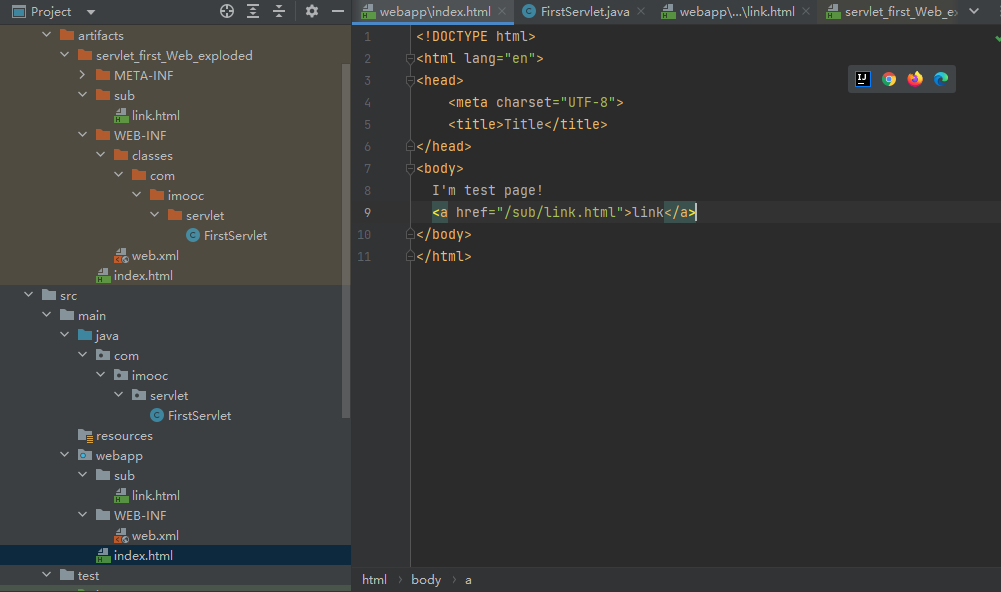
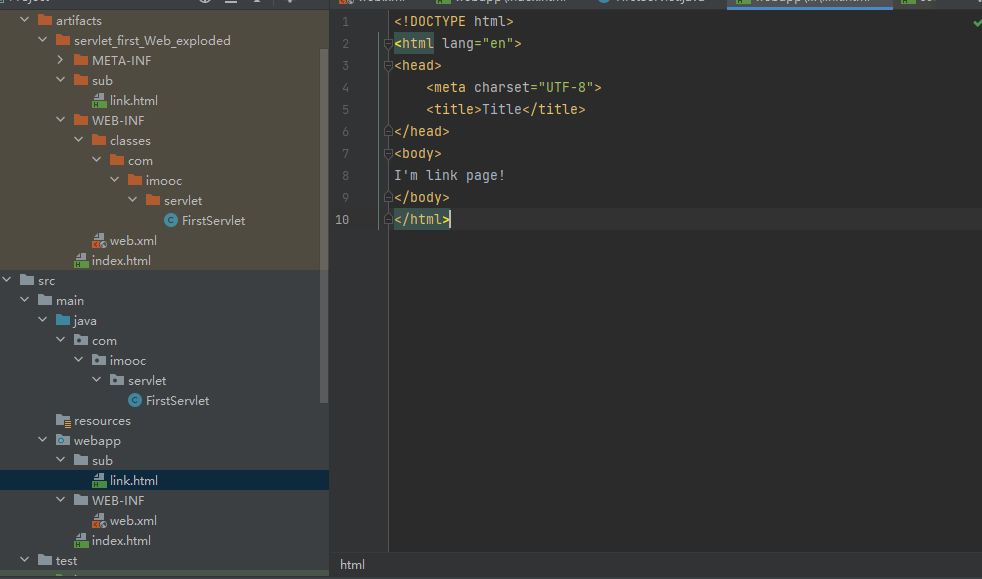
JavaWeb工程标准结构




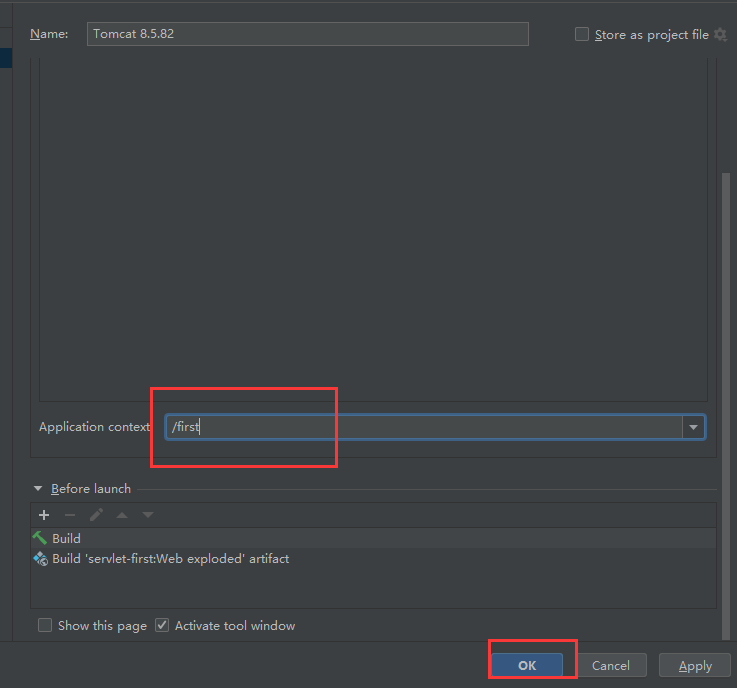
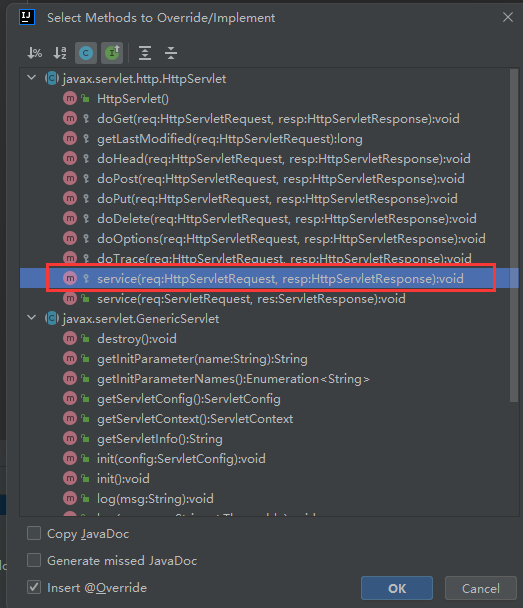
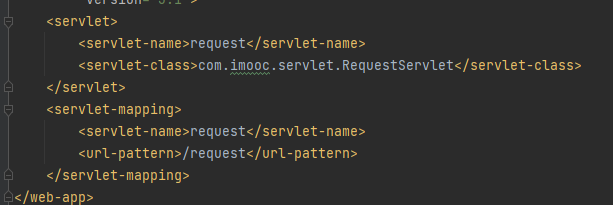
Servlet的开发和基本配置
Servlet开发步骤
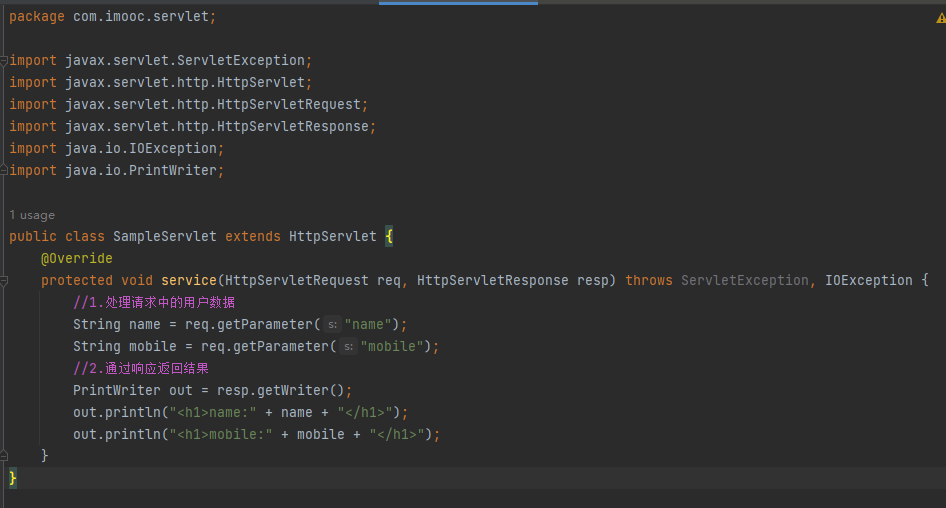
创建Java类,继承HttpServlet
重写service方法,处理请求,生成响应
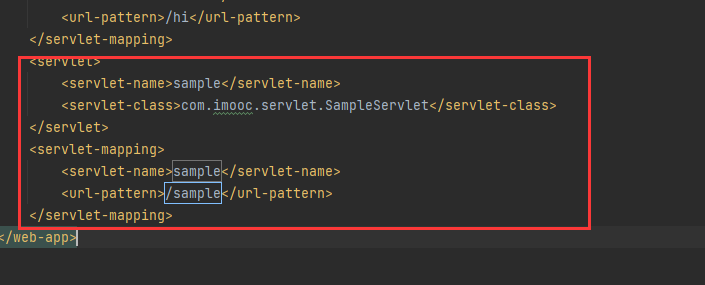
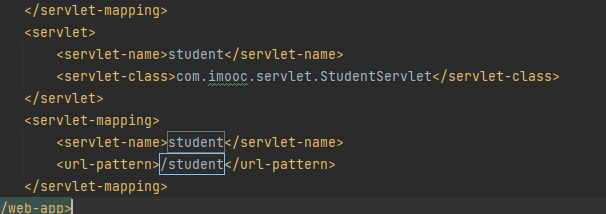
配置web.xml,绑定访问地址



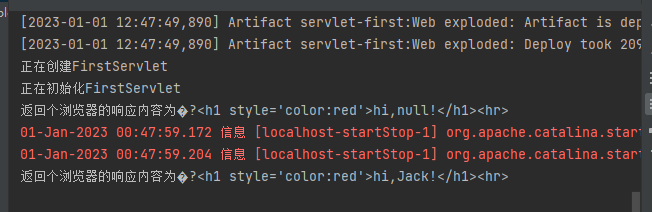
请求参数的发送与接收
请求参数
请求参数是指浏览器通过请求向Tomcat提交的数据
请求参数通常是用户输入的数据,待Servlet进行处理
参数名1=值1&参数名2=值2&参数名n=…
Servlet接收请求参数
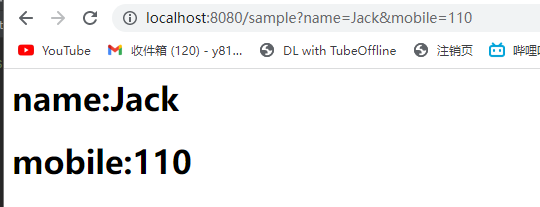
request.getParameter() -接收单个参数
request.getParameterValues() -接收多个同名参数
student.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>学员信息登记表</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>学员信息登记表</h1>
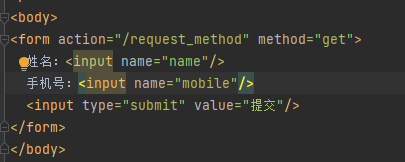
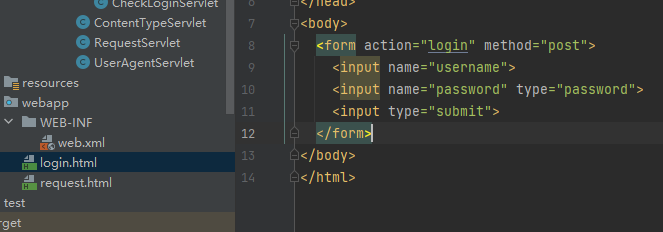
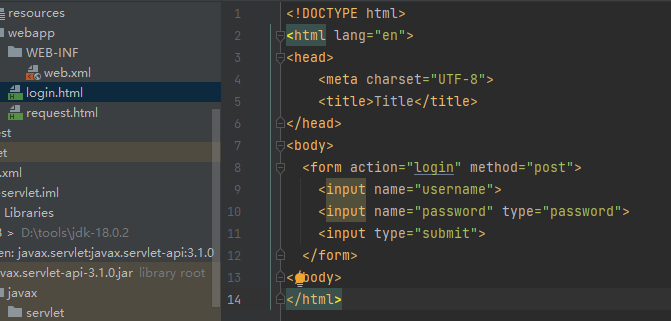
<form action="/student">
姓名:<input name="name"/>
<br/>
手机:<input name="mobile">
<br/>
性别:
<select name="sex" style="width: 100px;padding: 5px;margin: 5px">
<option value="male">男</option>
<option value="female">女</option>
</select>
<br/>
特长:
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="English"/>英语
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="Program"/>编程
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="Speech"/>演讲
<input type="checkbox" name="spec" value="Swimming"/>游泳
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|



1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| package com.imooc.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
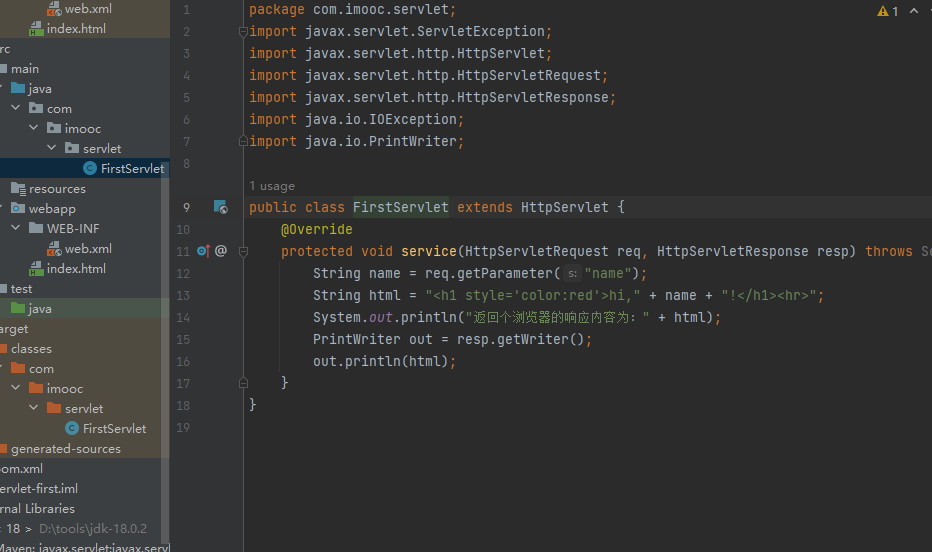
public class StudentServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
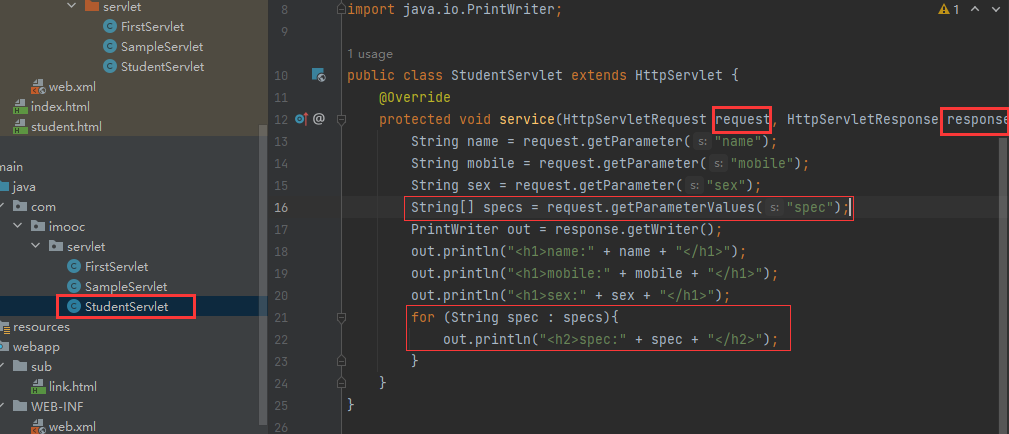
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String mobile = request.getParameter("mobile");
String sex = request.getParameter("sex");
String[] specs = request.getParameterValues("spec");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<h1>name:" + name + "</h1>");
out.println("<h1>mobile:" + mobile + "</h1>");
out.println("<h1>sex:" + sex + "</h1>");
for (String spec : specs){
out.println("<h2>spec:" + spec + "</h2>");
}
}
}
|



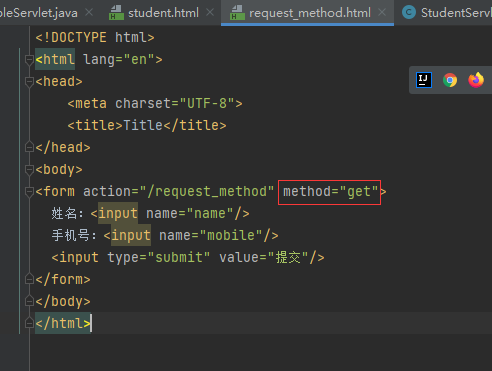
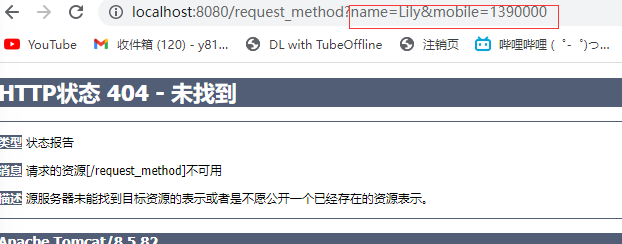
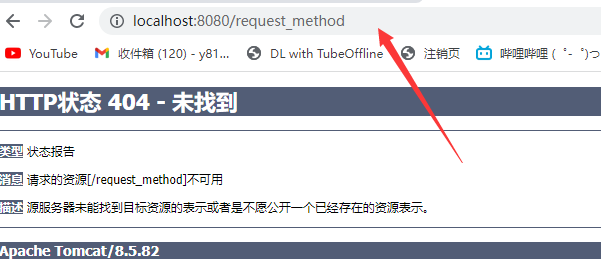
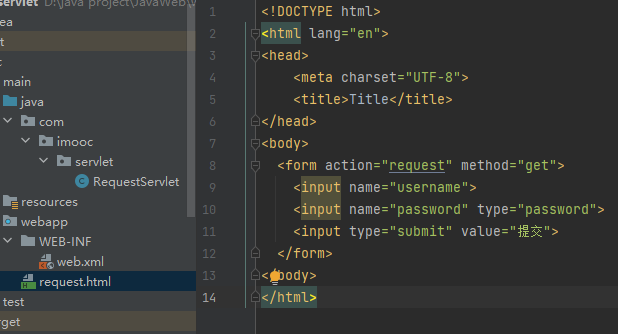
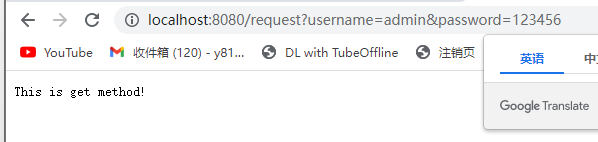
Get与Post请求方式
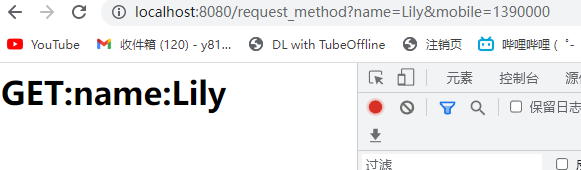
Get方式将请求参数附加在访问地址后显性向服务器发送的方式。
http://localhost:8080/sample?name=zhangsan
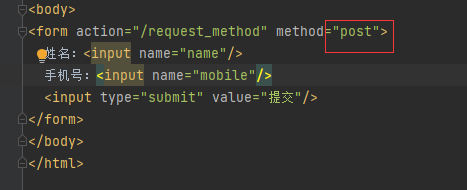
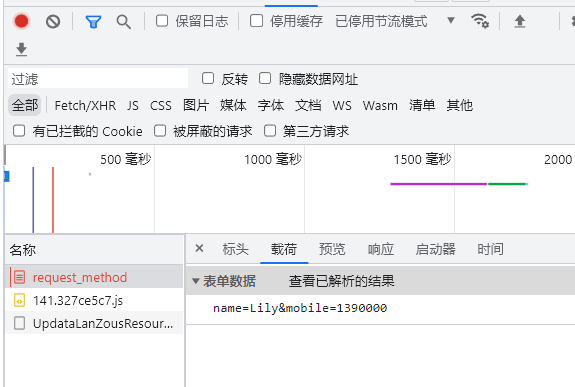
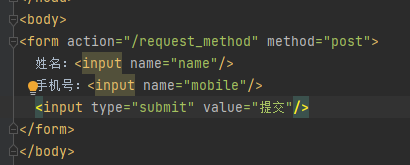
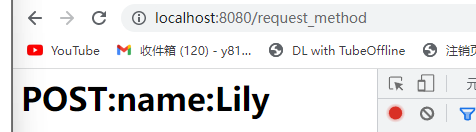
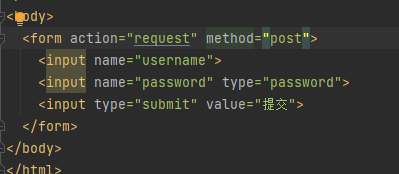
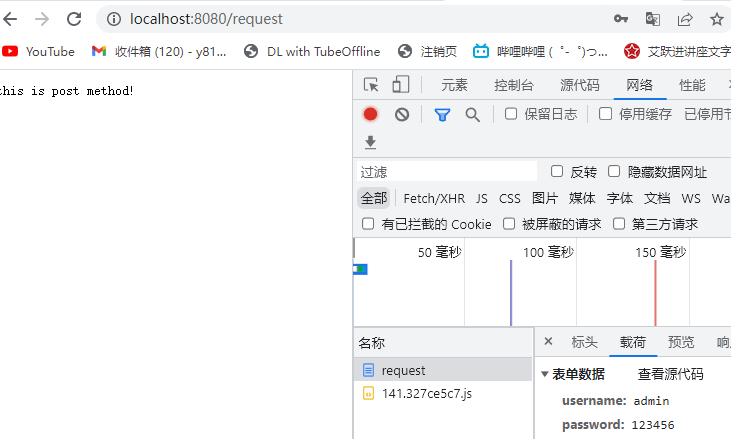
Post方式会将数据放在“请求体”中隐性向服务器发送的方式
http://localhost:8080/sample
请求体:name=zhangsan
Get常用于不包括敏感信息的查询功能
例如:http://www.baidu.com/s?wd=imooc&rsv_spt=1
Post用于安全性要求较高的功能或者服务器的“写”操作





Get与Post处理方式
所有请求 -service()方法
Get请求 -doGet()方法
Post请求 -doPost()方法

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| package com.imooc.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
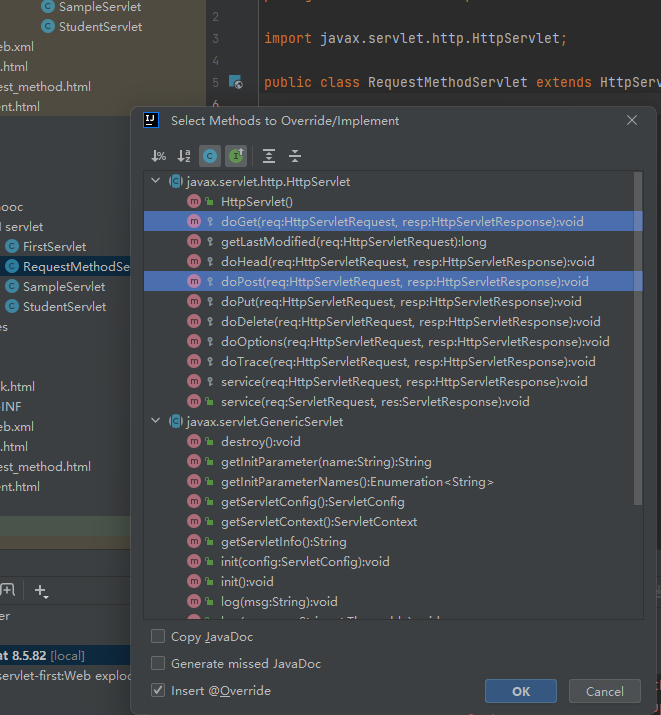
public class RequestMethodServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = req.getParameter("name");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.println("<h1>GET:name:" + name + "</h1>");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = req.getParameter("name");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.println("<h1>POST:name:" + name + "</h1>");
}
}
|





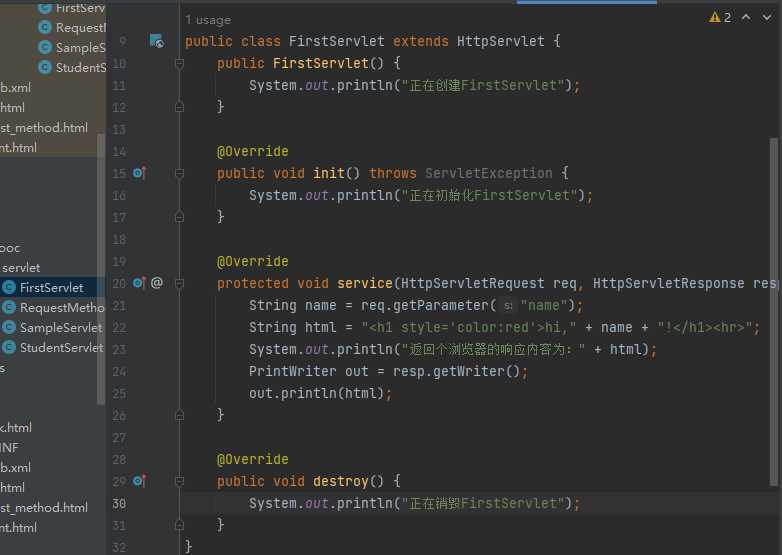
Servlet生命周期
装载 - web.xml
创建 - 构造方法
初始化 - init()
提供服务 - service()
销毁 - destory()

Alt+insert 选择第一个




关闭销毁

这是利用多线程方式运行。
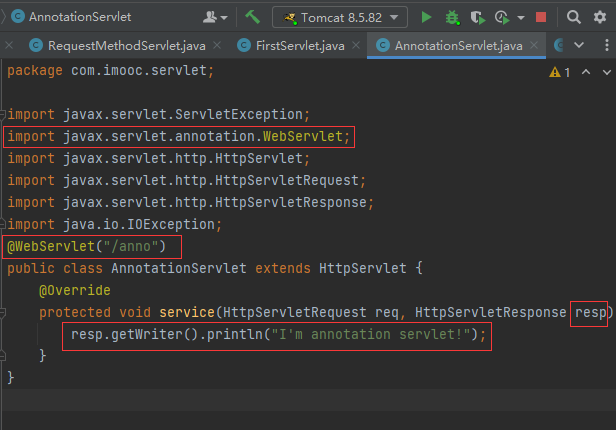
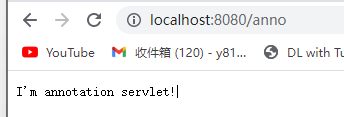
使用注解配置Servlet
Servlet 3.x 之后引入了“注释Annotation” 特性
注解用于简化Web应用程序的配置过程
Servlet核心注解:@WebServlet


Servlet进阶

WEB请求与响应解析
请求的结构
URL与URI
URL统一资源定位符,表示Web应用对外暴露的访问地址
示例: http://www.baidu.com/index.html
URI统一资源标示符,表示Web应用资源的访问路径
示例: /index.html
HTTP请求的结构









利用请求开发多端应用
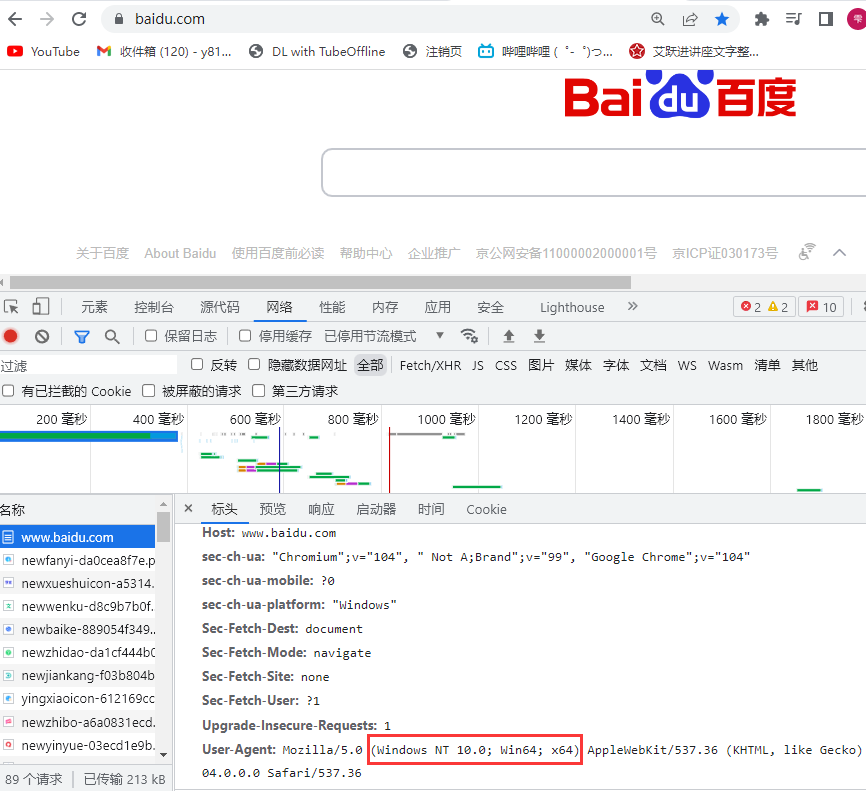
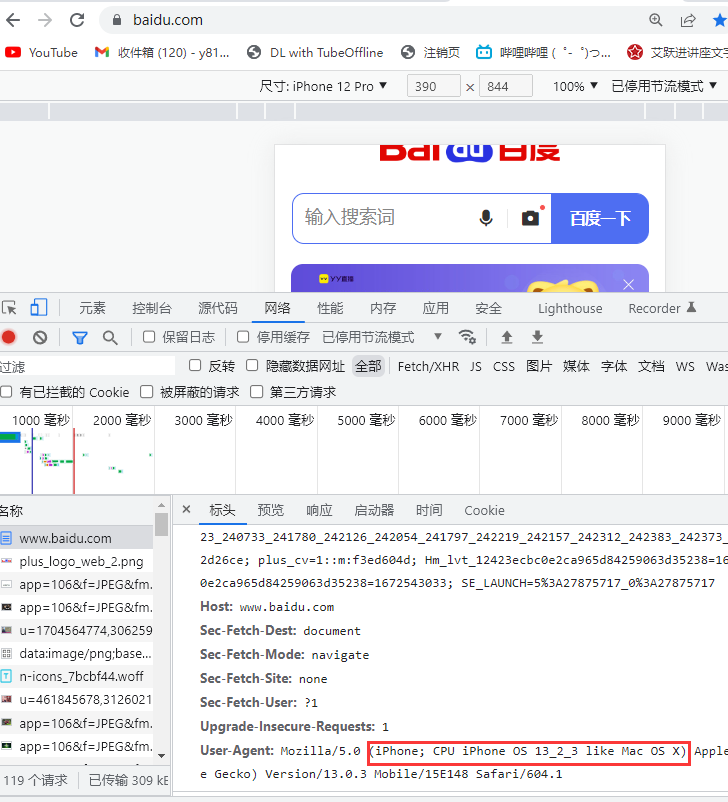
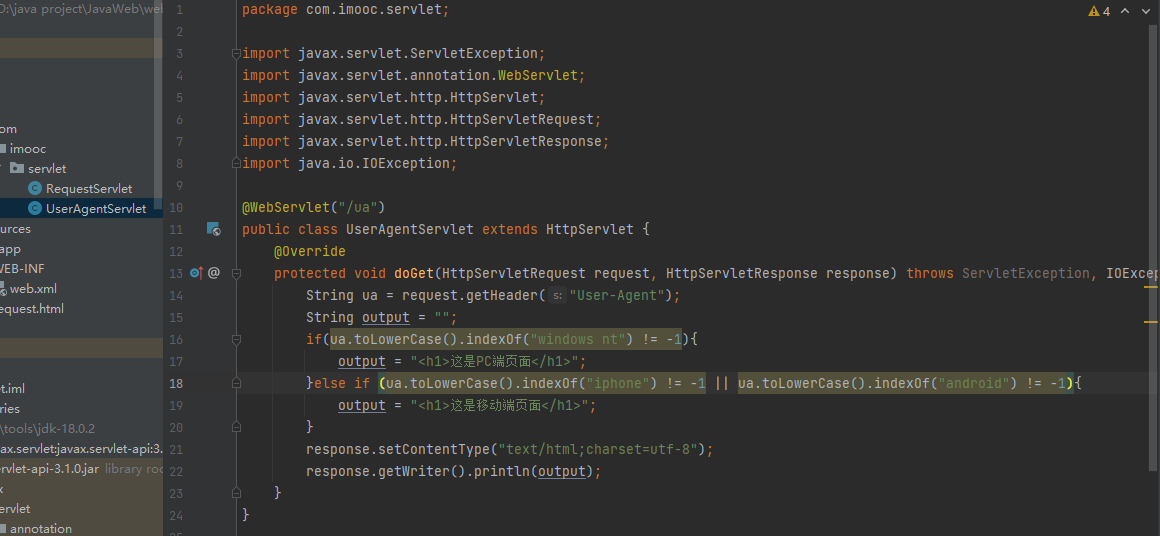
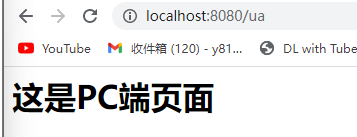
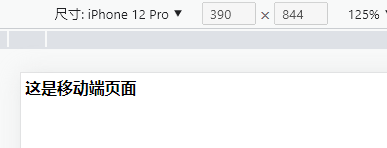
巧用请求头开发多端应用









1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| package com.imooc.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
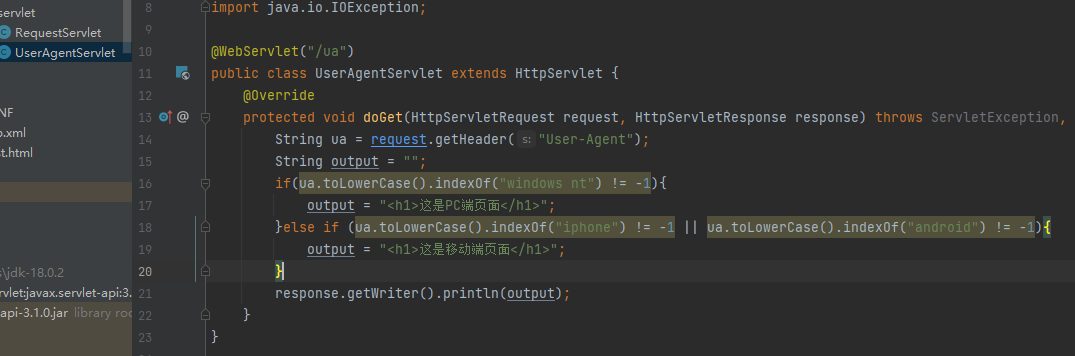
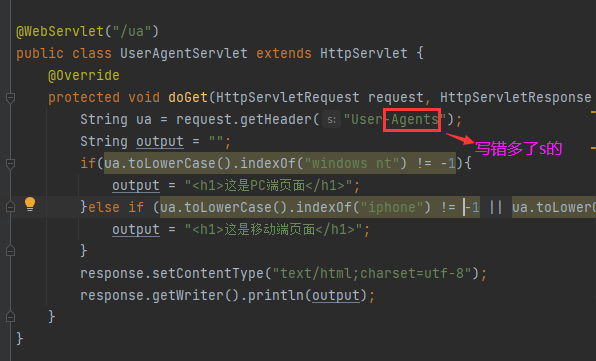
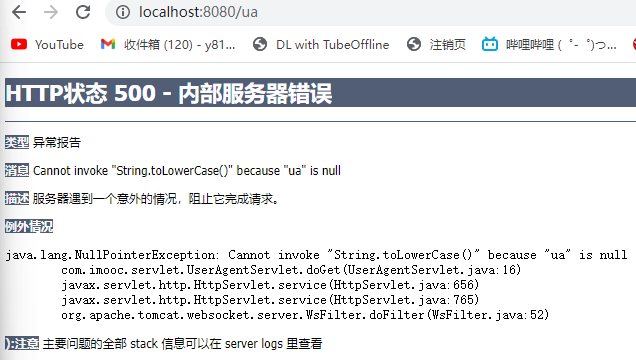
@WebServlet("/ua")
public class UserAgentServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
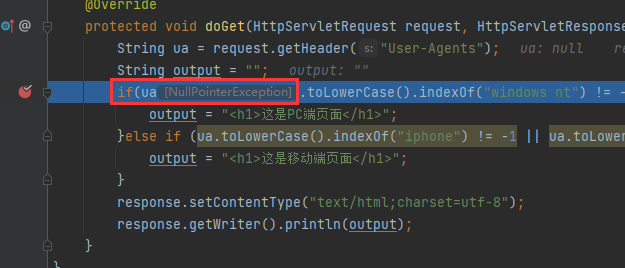
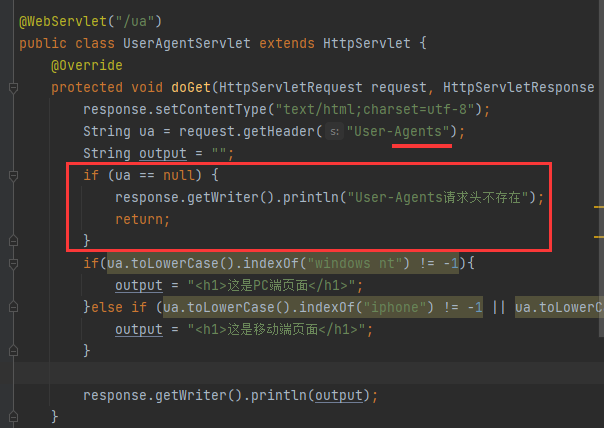
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String ua = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
String output = "";
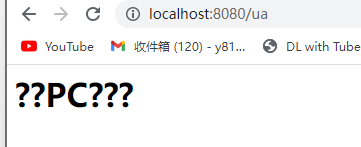
if(ua.toLowerCase().indexOf("windows nt") != -1){
output = "<h1>这是PC端页面</h1>";
}else if (ua.toLowerCase().indexOf("iphone") != -1 || ua.toLowerCase().indexOf("android") != -1){
output = "<h1>这是移动端页面</h1>";
}
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().println(output);
}
}
|
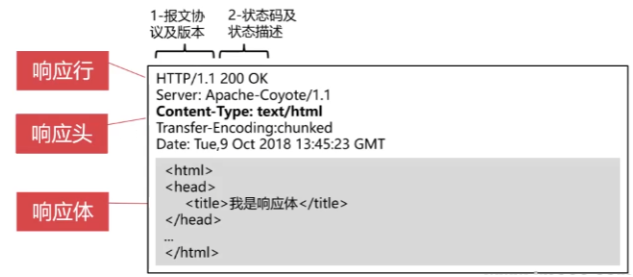
响应的结构
HTTP响应应包含三部分:响应行、响应头、响应体

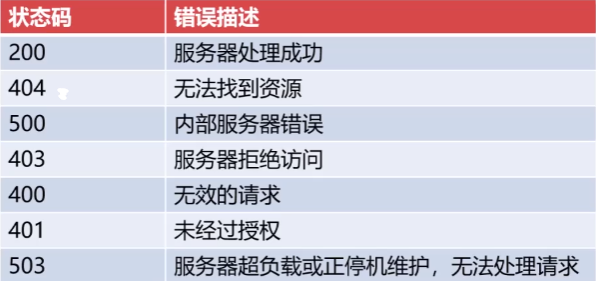
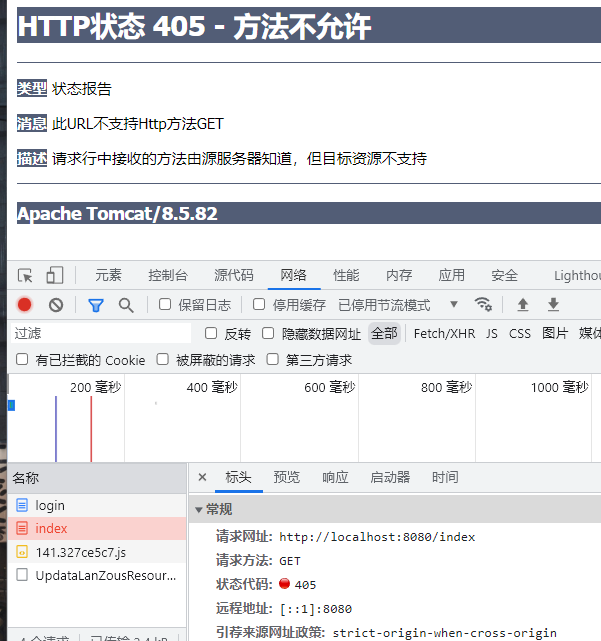
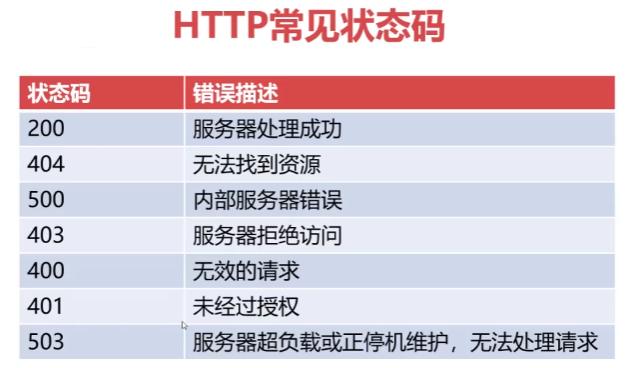
HTTP常见状态码






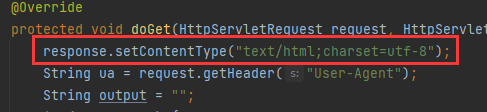
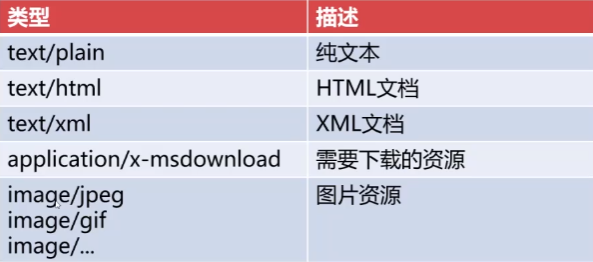
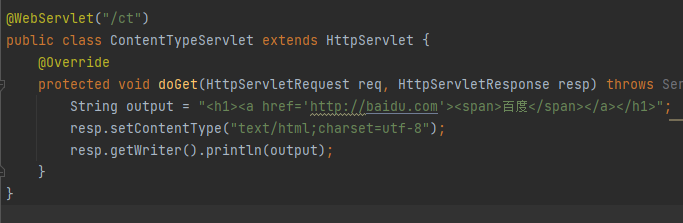
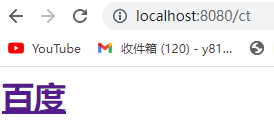
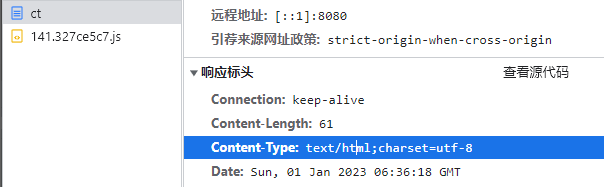
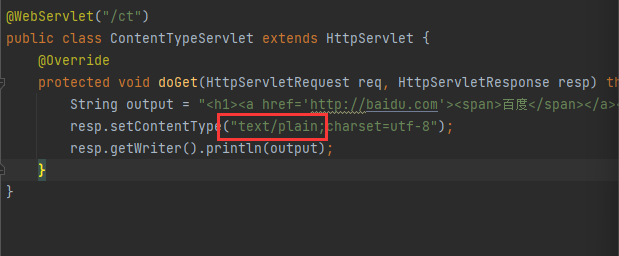
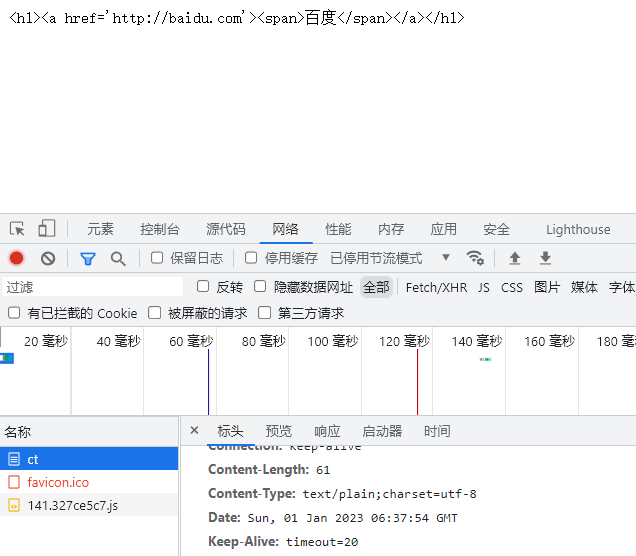
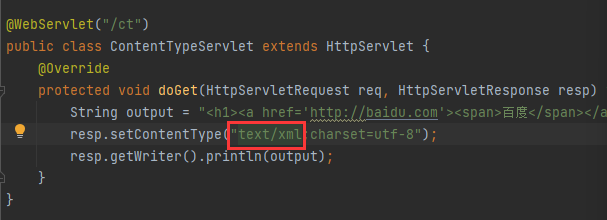
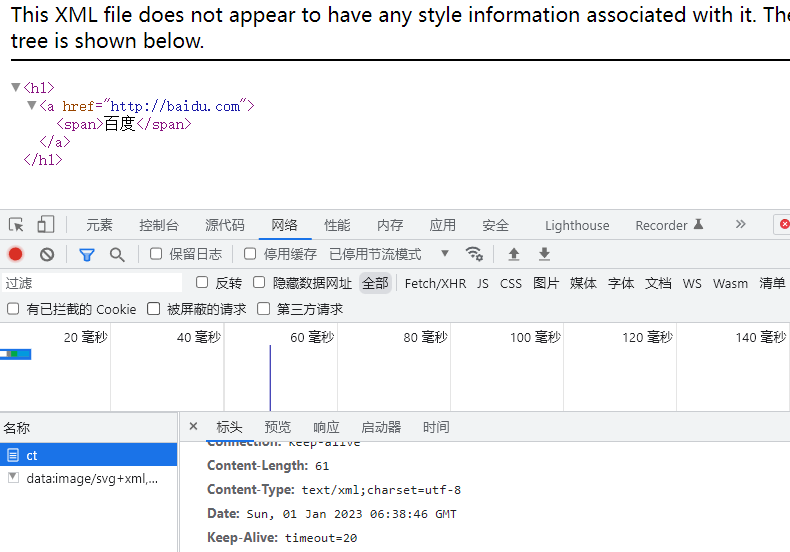
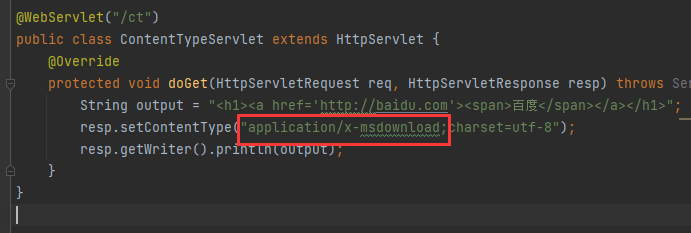
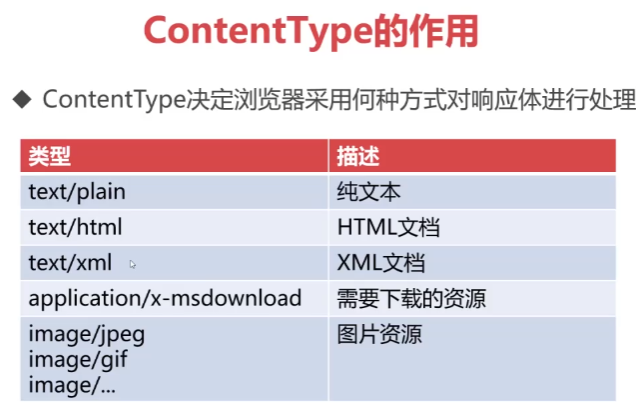
ContentType的作用

ContentType绝对浏览器采用何种方式对响应体进行处理











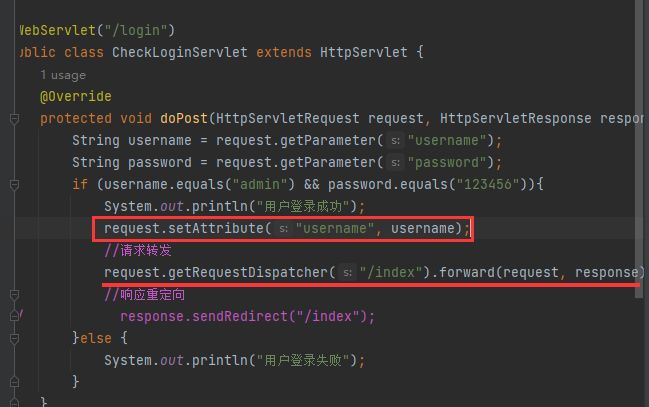
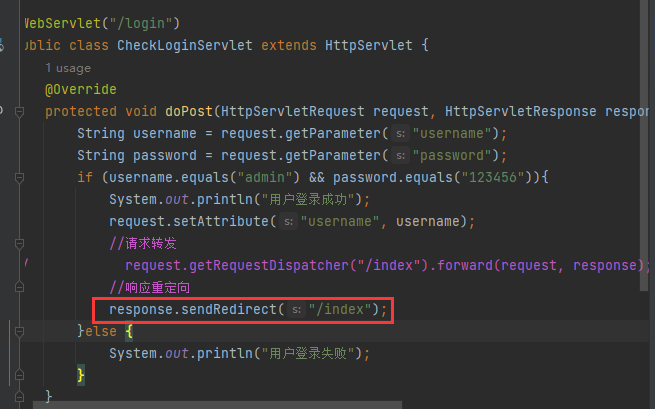
请求转发与响应重定向
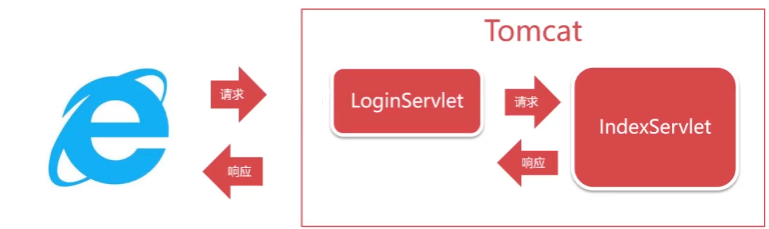
多个Servlet之间跳转有两种方式:
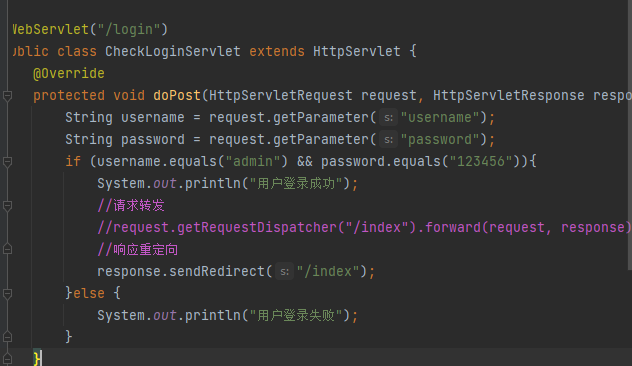
request.getRequestDispatcher().forward - 请求转发
response.sendRedirect - 响应重定向




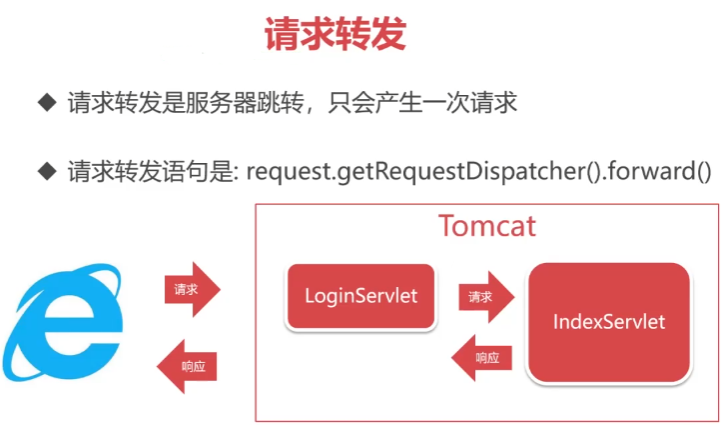
请求转发





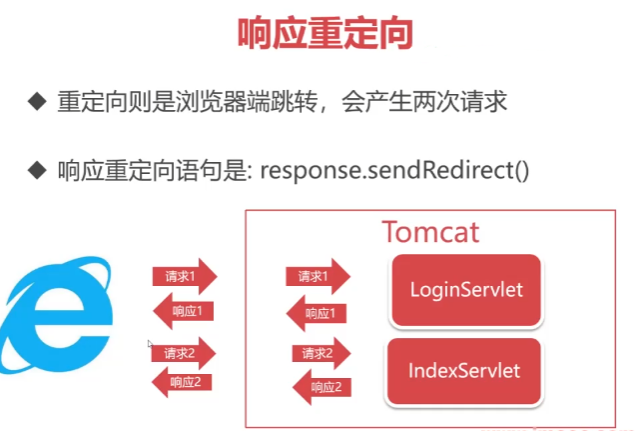
响应重定向


解决405要在/index中在添加doGet方法

但,这是蠢方法,可以改成以下方法


请求转发与重定向的原理
请求转发
请求转发是服务器跳转,只会产生一次请求
请求转发的语句是:request.getRequestDispatcher().forward()

响应重定向
重定向则是浏览器端跳转,会产生两次请求
响应重定向语句是:response.sendRedirect()

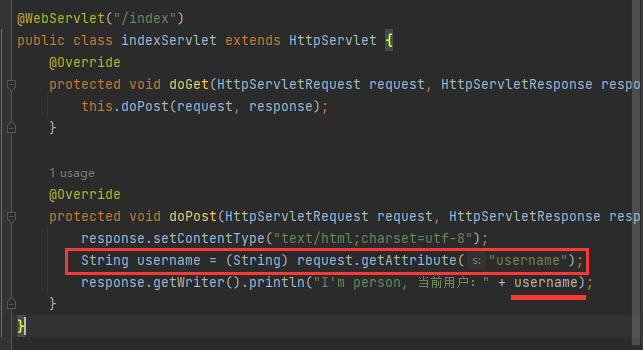
设置请求自定义属性
请求允许创建自定义属性
设置请求属性:request.setAttribute(属性名, 属性值)
获取请求属性:Object attr = request.getAttribute(属性名)





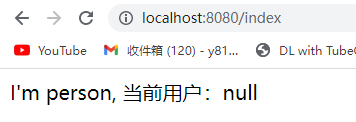
请求自定义属性不能用响应重定向。
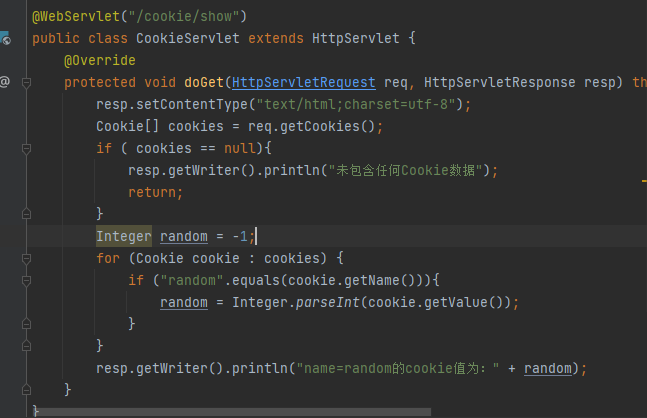
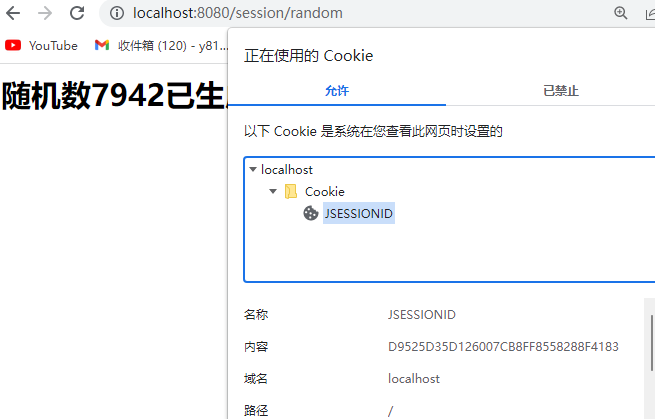
Session与ServletContext原理
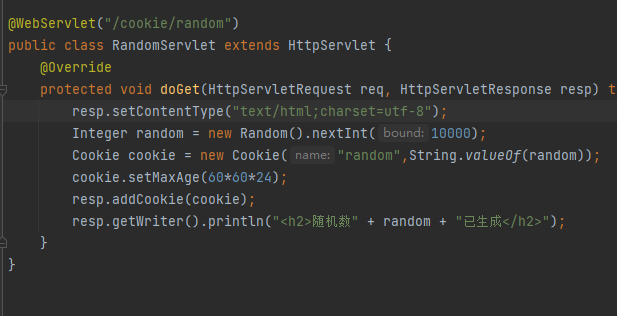
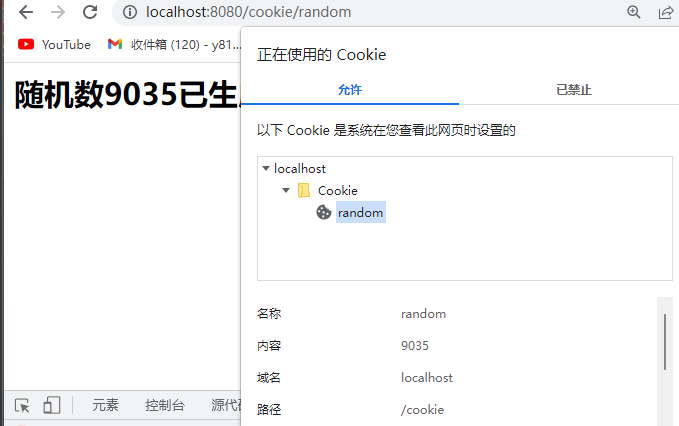
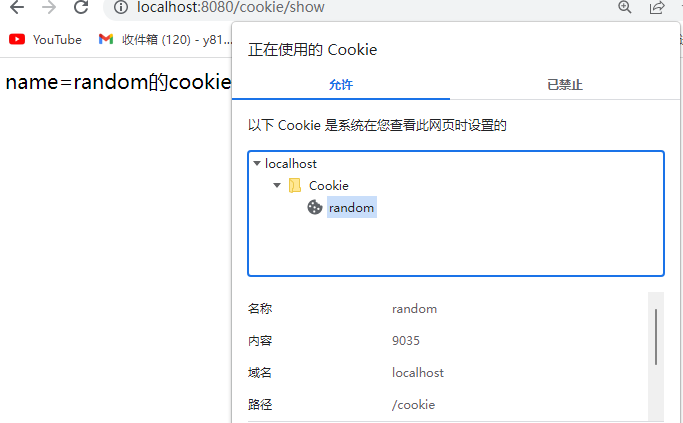
浏览器Cookie
默认是本次浏览器窗口关闭就失效,





默认cookie的生成时间是和当前浏览器的进程保持一致。

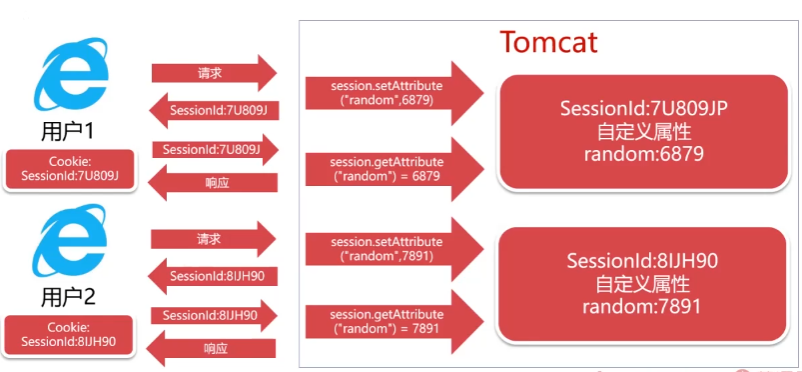
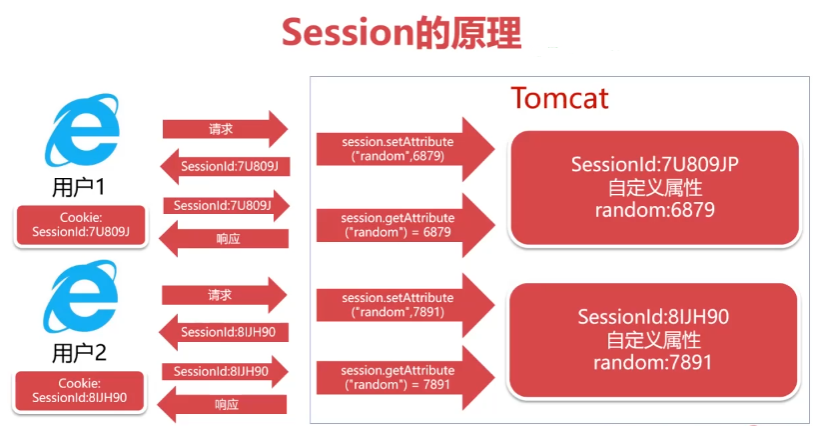
Session-用户会话
Session(用户会话)用于保存与“浏览器窗口”对应的数据
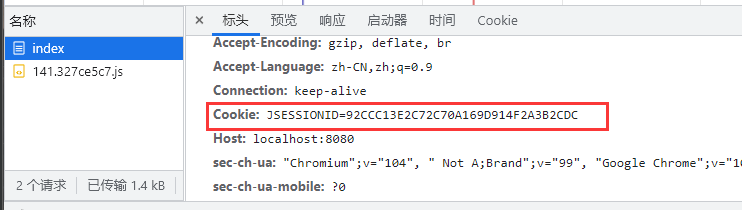
Session的数据存储在Tomcat服务器的内存中,具有时效性
Session通过浏览器Cookie的SessionId值提取用户数据
Session常用方法
request.getSession() - 获取Session对象
get|set|removeAttribute() -获取|设置|删除Session属性
setMaxInactiveInterval() - 设置Session超时时间 (默认存在30分钟)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| package com.imooc.servlet.session;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
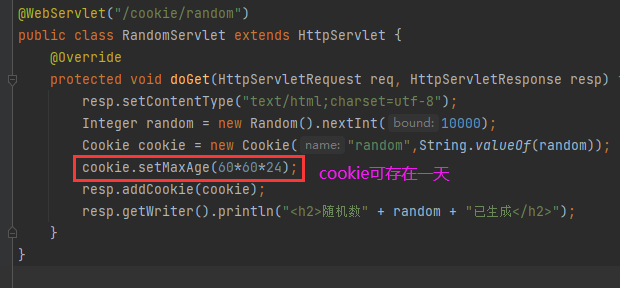
@WebServlet("/session/random")
public class RandomServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Integer random = new Random().nextInt(10000);
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.setAttribute("random", random);
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().println("<h2>随机数" + random + "已生成</h2>");
}
}
|

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package com.imooc.servlet.session;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/session/show")
public class SessionServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
Integer random = (Integer) session.getAttribute("random");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
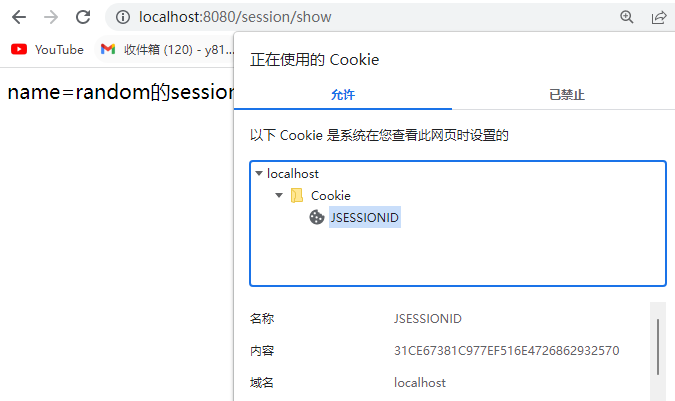
resp.getWriter().println("name=random的session值为:" + random);
}
}
|

Session的执行原理
Session的原理

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| package com.imooc.servlet.forward;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
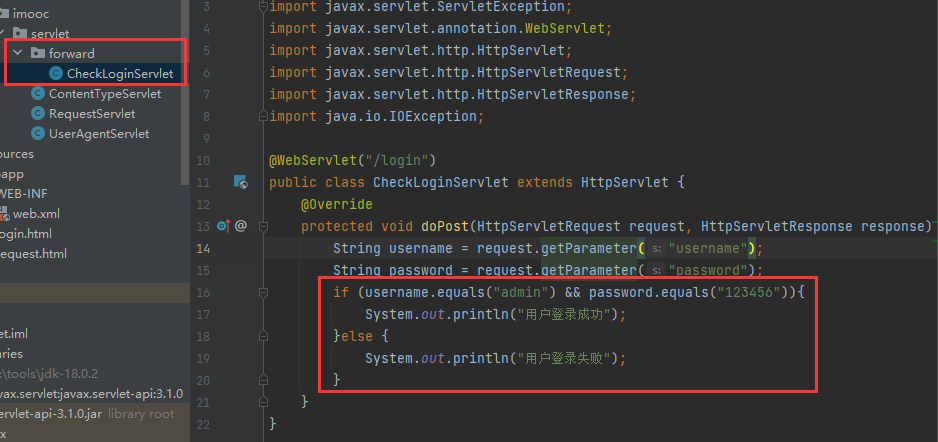
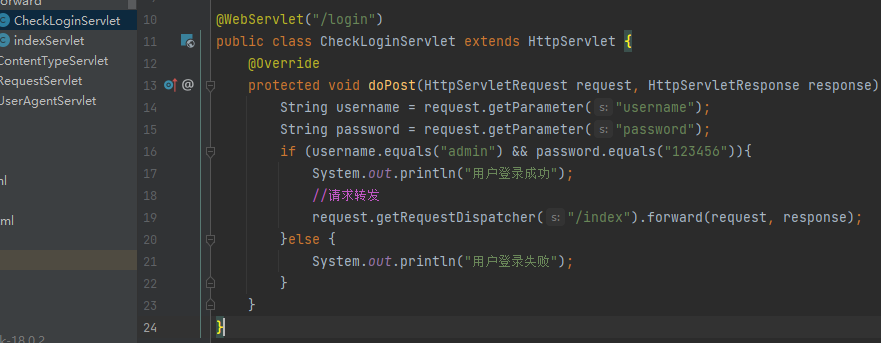
@WebServlet("/login")
public class CheckLoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
if (username.equals("admin") && password.equals("123456")){
System.out.println("用户登录成功");
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("username", username);
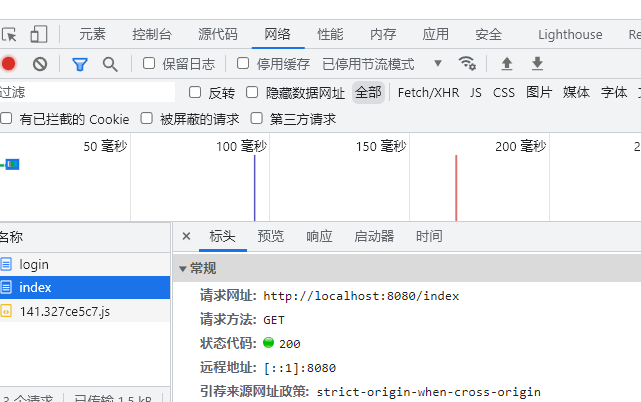
response.sendRedirect("/index");
}else {
System.out.println("用户登录失败");
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| package com.imooc.servlet.forward;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
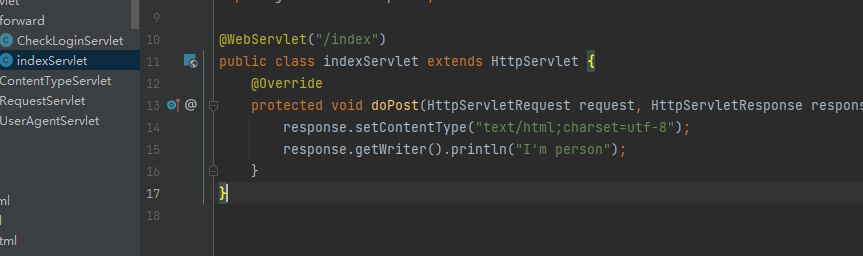
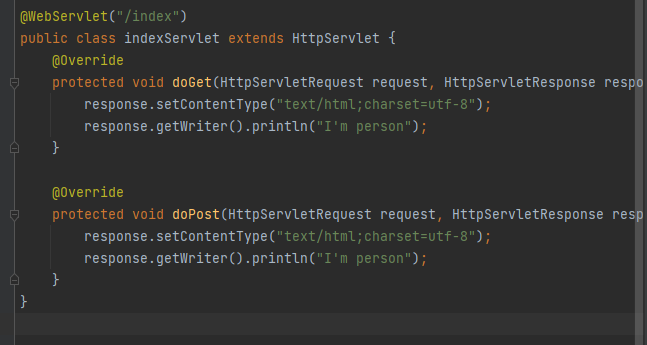
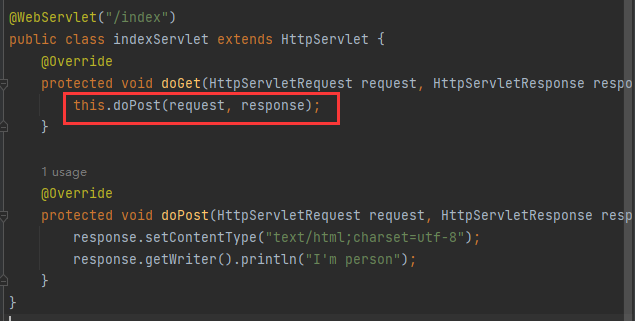
@WebServlet("/index")
public class indexServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(request, response);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
String username = (String) session.getAttribute("username");
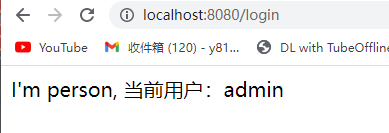
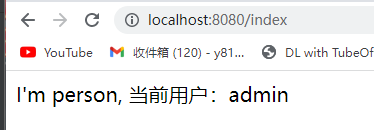
response.getWriter().println("I'm person, 当前用户:" + username);
}
|



ServletContext与三大作用域对象
ServletContext
ServletContext(Servlet上下文对象),是Web应用全局对象
一个Web应用只会创建一个ServletContext对象
ServletContext随着Web应用启动而自动创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package com.imooc.servlet.servletcontext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/servletContext/init")
public class ServletInitServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = req.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("copyright", "Copyright 2021 exp.com 京ICP备 12003892号-11 公网安备11010802030151号");
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
resp.getWriter().println("ServletContext已初始化");
}
}
|

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| package com.imooc.servlet.servletcontext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
@WebServlet("/servletContext/index")
public class IndexServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
ServletContext context = req.getServletContext();
String copyright = (String) context.getAttribute("copyright");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
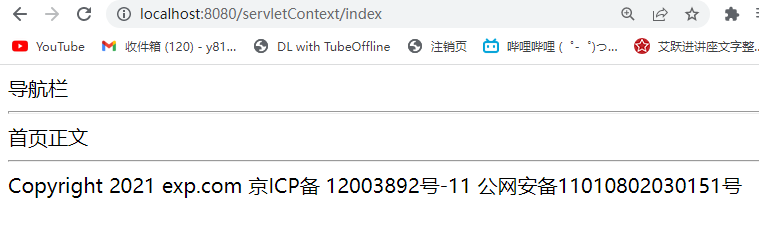
out.println("导航栏");
out.println("<hr/>");
out.println("首页正文");
out.println("<hr/>");
out.println(copyright);
}
}
|

Java Web三大作用域对象
HttpServletRequest - 请求对象
HttpSession - 用户会话对象
ServletContetx - Web应用全局对象
以上作用范围按从小到大排序。
Servlet开发应用实践
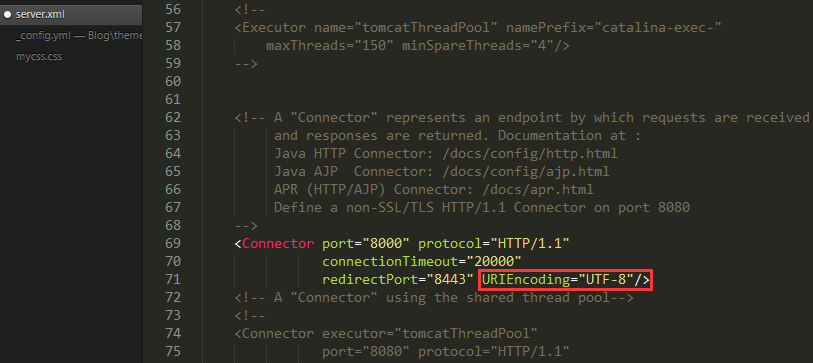
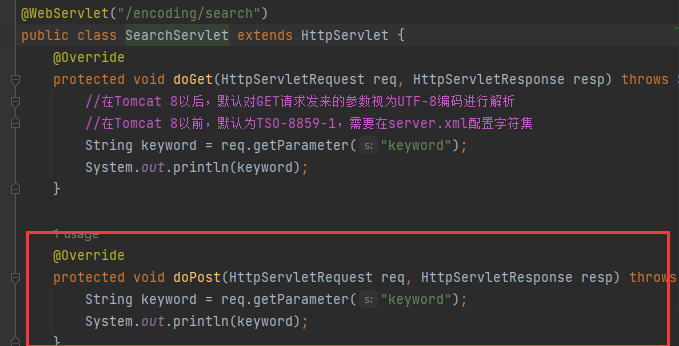
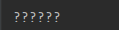
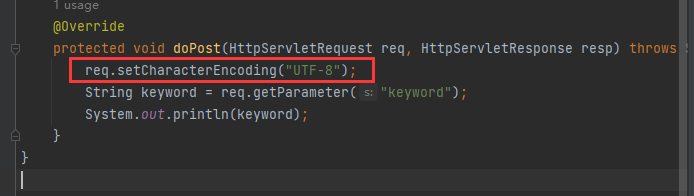
Web应用的中文乱码由来
发送方与接收方对数据使用不同的字符集解析就会产生乱码
解决乱码的思路是保证浏览器与服务器统一为UTF-8编码即可
在Servlet中请求与响应都需要设置UTF-8字符集







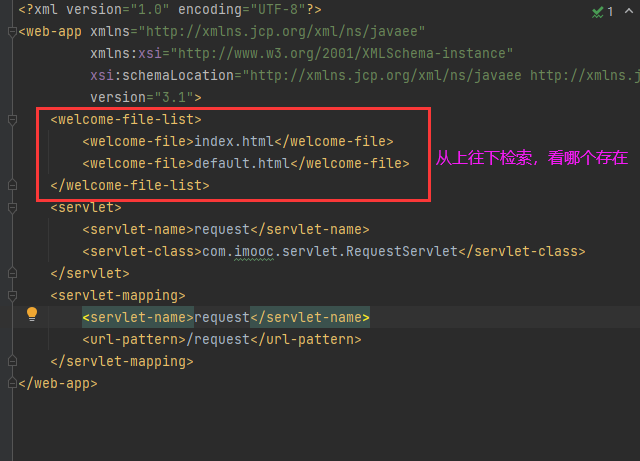
web.xml配置默认首页与通配符映射
web.xml常用配置
修改web应用默认首页
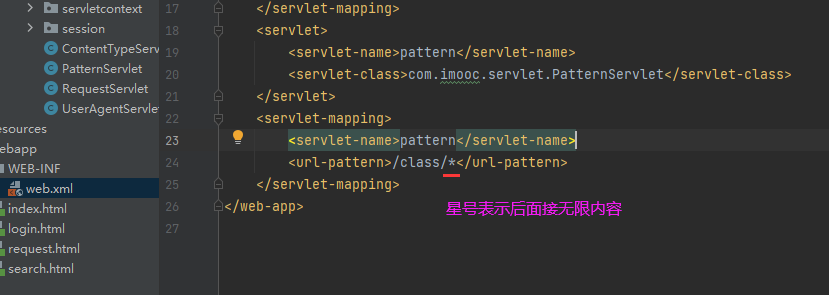
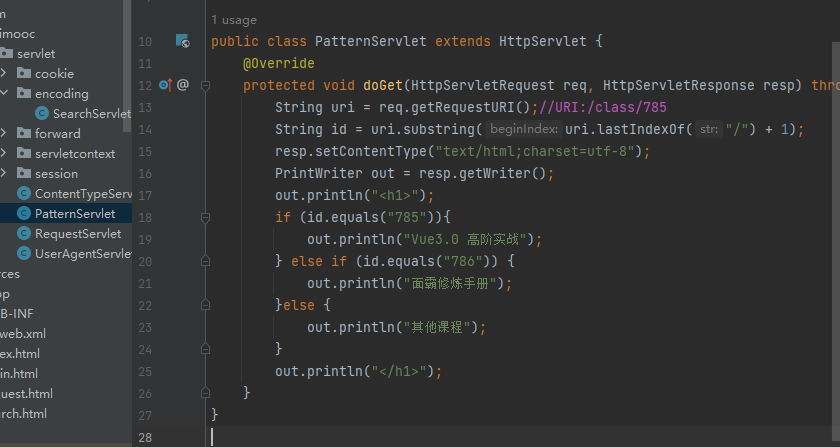
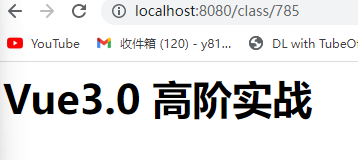
Servlet 通配符映射及初始化参数
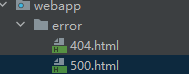
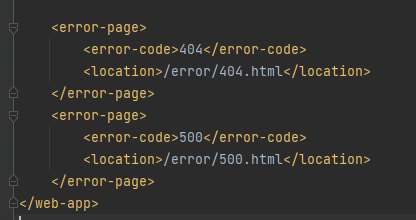
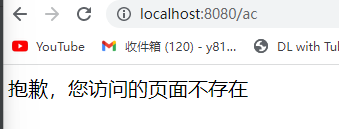
设置404、500等状态码默认页面



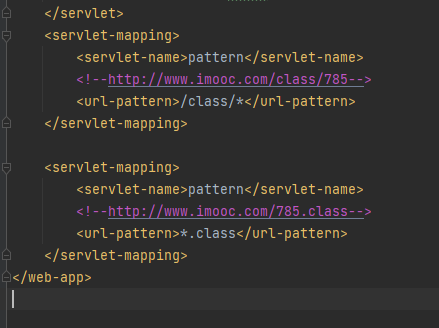
常见的URL用法





但前缀加后缀是错误的。

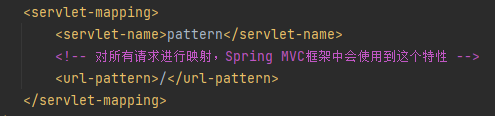
对所有请求进行映射,后面不用加*

Servlet启动时加载与错误页面设置
启动时加载Servlet
1
2
3
4
5
| web.xml使用<load-on-startup>设置启动加载
<load-on-startup>0~9999</load-on-startup>
启动时加载在工作中常用于系统的预处理
|

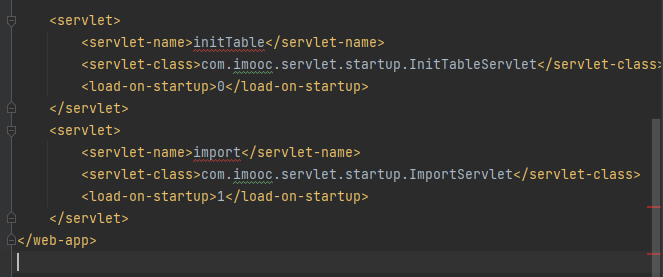
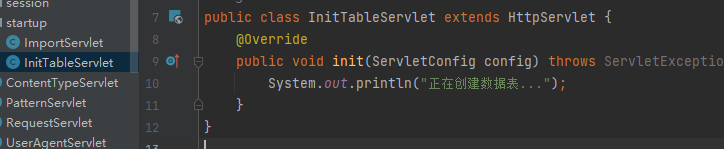
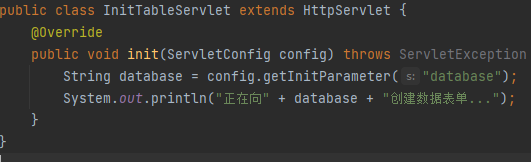
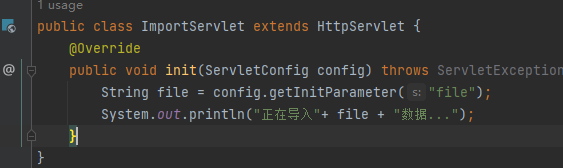
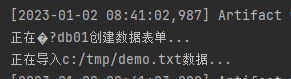
InitTableServlet用于建表
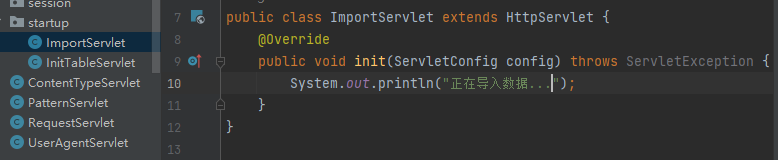
ImportServlet用于导入数据

InitTableServlet也同样

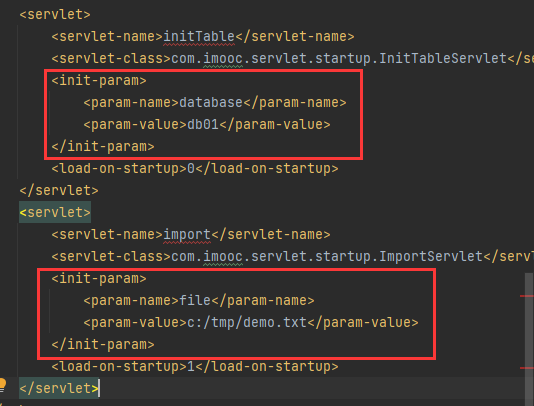
配置web.xml,这里提示要mapping,但只要到他的启动时加载功能。
而load-on-startup数值大小决定着运行顺序。







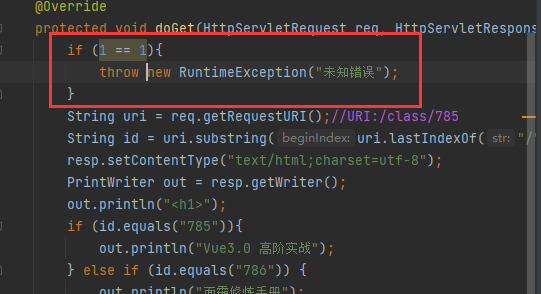
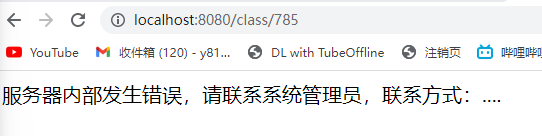
自定义错误页面







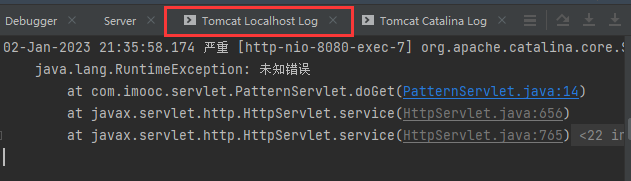
而错误在后台log中显示

JavaWeb应用打包与发布
Java Web应用采用war包进行发布
发布路径为:{TOMCAT_HOME}/webapps
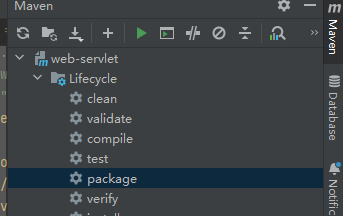
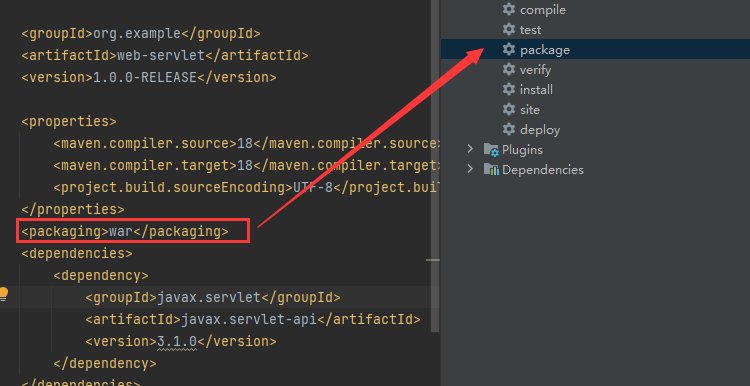
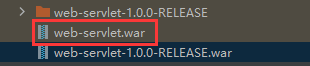
利用Maven实现war包导出

直接点这生成的是jar包,但我们要的是war包
于是要加入一行代码

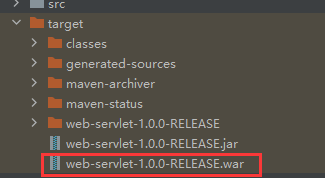
在点击生成war包到target目录下
报Cannot access defaults field of Properties错误的话
在pom.xml中在加入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
|




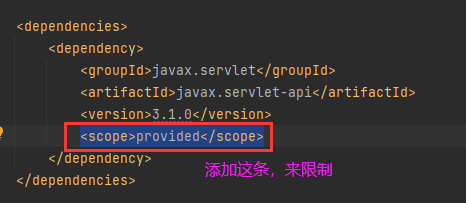
可发现之前里面包含jar包的lib目录消失了。
Maven的Scope属性

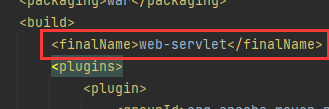
改最终导出名


发布

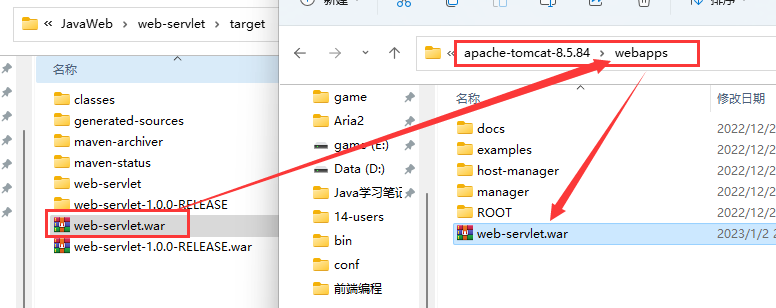
最后将该war包转移到tomcat目录下webapps中即外部应用的发布就完成了。
打开startup.bat

自动解压出来。
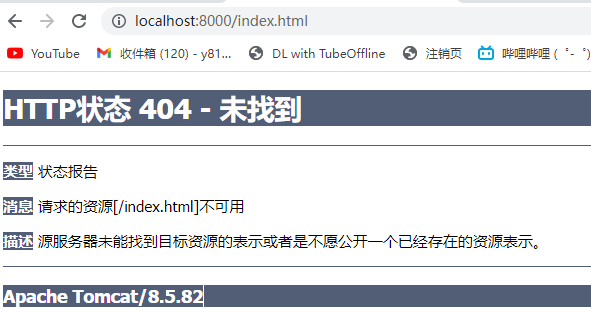
在地址栏输入http://localhost:8000/index.html

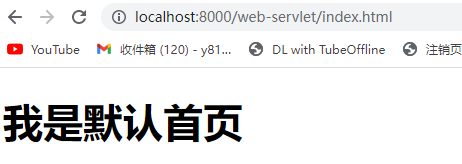
这里解压缩后添加了上下文,所以还得添加/web-servlet
http://localhost:8000/web-servlet/index.html

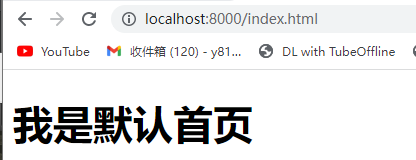
如果没响应,打开shutdown.bat再启动

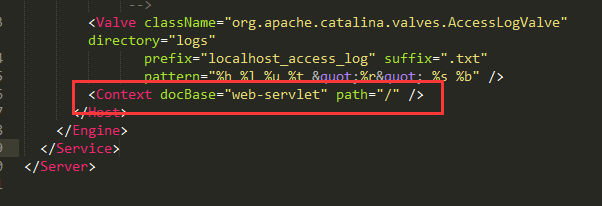
在tomcat的conf中server.xml最下面那加入这条可删除上下文。

总结